
Remote Broadcasting: Transforming Live Streaming on OTT Platforms
For a second, forget expensive satellite trucks and limited reach. Imagine broadcasting live to the world from anywhere with an internet connection.
That's the power of remote broadcasting—transforming how creators and TV operators deliver live streaming experiences through OTT platforms.
In this article, we’ll talk about the impact of remote broadcasting, covering its definition, use cases, technologies, benefits, best practices, and how inoRain ensures a seamless remote broadcast experience.
What is Remote Broadcasting?
Remote broadcasting is a method of producing and delivering live video content from virtually any location, eliminating traditional infrastructure constraints.
Remote broadcasting involves capturing video and audio feeds, encoding them for streaming, transmitting them over IP networks, and distributing them to viewers via OTT services.
Definition and Evolution
Remote broadcasting began as a simple extension of traditional broadcasting, relying on satellite uplinks and dedicated transmission lines.
Today, it has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem that uses cloud technology, AI-driven automation, and advanced compression algorithms, empowering you to transmit high-quality live video and audio feeds from any location with internet access.
Now, remote broadcasting solutions offer features once exclusive to professional broadcast studios, such as multi-camera switching, real-time graphics overlays, and cloud-based collaborative editing.
This evolution enables independent creators, brands, and broadcasters to deliver professional-grade productions with minimal resources.
How Remote Broadcasting Works
Remote broadcasting works using cloud-based technologies and internet connectivity to transmit live video and audio feeds from remote locations to viewers via OTT platforms.
Here’s the process in five simple steps:
Step 1: Video and audio signals are captured from cameras and microphones at the remote location.
Step 2: The captured signals are then encoded into digital formats through a live streaming encoder, making them suitable for streaming over the internet.
Step 3: Next, the encoded streams are transmitted over the internet to an OTT platform.
Step 4: The OTT platform then distributes the live streams to viewers across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers.
Step 5: Viewers can interact with the live streams through features like chat, polls, and Q&A sessions, creating a dynamic and engaging experience.
Remote Broadcasting Key Use Cases
Remote broadcasting transforms OTT live streaming across multiple industries, making high-quality live video production more efficient, cost-effective, and scalable.

Here’s how it’s revolutionizing various sectors:
1. Live Sports Production
Imagine broadcasting a live sports event with multiple camera angles, instant replays, and real-time commentary, all managed remotely from a single control room. No more massive crews and expensive equipment on-site.
Remote broadcasting makes this a reality, offering viewers a dynamic and engaging experience while significantly reducing production costs.
Multiple camera angles capture all the action, while instant replay and graphics integration enhance the viewing experience. Simultaneous multi-language commentary feeds cater to a global audience, expanding reach and engagement.
2. News Gathering
Picture a news reporter broadcasting live from the scene of a breaking story without the need for a bulky satellite truck.
Remote broadcasting transforms traditional news gathering, enabling reporters to broadcast live from anywhere with internet connectivity. This mobile streaming solution supports real-time collaboration between field teams and studio producers, ensuring up-to-the-minute coverage. It integrates with social media feeds, live audience interactions, and boosts engagement, allowing immediate feedback.
3. Virtual Events
Hybrid conferences, concerts, and industry expos now offer both in-person and remote participation, breaking geographical barriers.
Remote broadcasting allows for:
- Seamless integration of remote speakers and performers.
- Real-time audience participation, including Q&As and polls.
- Simultaneous translation and closed captioning for inclusivity.
4. Educational Content
Step into a classroom where students from diverse locations can participate in live lectures, interact with the instructor in real-time, and even experience virtual laboratory demonstrations. Remote live production makes this all possible.
It supports distance learning, making education more accessible and engaging. Global collaboration between educational institutions becomes easier, fostering a richer learning environment for students.
5. Entertainment Production
Reality shows, live performances, and interactive programs can now be produced with minimal on-site crews while maintaining high production quality. Remote video streaming supports:
- Real-time audience feedback, allowing creators to adjust content dynamically.
- Hybrid production models, blending remote and on-site elements for greater flexibility.
- Cost-effective remote workflows, reducing operational expenses without sacrificing quality.
6. Emerging Use Cases
The possibilities of remote broadcasting continue to expand. Imagine remote medical procedures being broadcast via 5G networks for ultra-low latency transmission, enabling collaboration between specialists across the globe.
Virtual production integration, which enables the real-time compositing of remote talent with virtual sets, opens up new creative avenues for filmmakers and content creators. AI-driven autonomous production for smaller-scale events promises to streamline workflows and further reduce costs.
Technologies Behind Remote Broadcasting
Remote broadcasting enables high-quality, reliable, and secure live streaming over OTT platforms. These advancements have eliminated the need for on-site production teams and expensive transmission infrastructure.
Here are the technology backbones of remote broadcasting:
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Modern remote broadcasting systems use advanced adaptive bitrate streaming technology to ensure optimal viewing experiences.
Adaptive bitrate streaming technology continuously monitors viewer connection speeds and automatically adjusts video quality to prevent buffering while maintaining the highest possible quality.
Adaptive bitrate streaming implements:
- Multi-bitrate encoding that creates multiple quality versions of the same content.
- Real-time quality switching based on viewer network conditions.
- Buffer management to prevent playback interruptions.
- Quality analytics to optimize delivery parameters.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A robust CDN infrastructure plays a crucial role in transforming how remote broadcasts reach global audiences.
A CDN is a system of interconnected servers strategically located around the world that store and deliver digital content from a server located closest to the user.
Modern CDN solutions provide:
- Global server networks that cache and deliver content from locations closest to viewers.
- Load balancing capabilities to handle sudden viewer surges.
- DDoS protection to maintain service availability.
- Edge computing capabilities for reduced latency.
- Real-time analytics for performance monitoring and optimization.
- Multi-CDN strategies for improved reliability.
Digital Rights Management (DRM) Protection
Ensuring content security in remote broadcasting requires advanced Digital Rights Management (DRM) solutions.
Modern DRM video streaming safeguards live and on-demand content while maintaining seamless playback across devices.
DRM solutions provide:
- End-to-end encryption to prevent unauthorized access and piracy.
- Device-specific security measures for platform-wide protection.
- Geographic restrictions to enforce regional content licensing.
- Viewer authentication protocols to verify user access rights.
- License delivery optimization for smooth, uninterrupted streaming.
- Real-time security monitoring to detect and counter threats instantly.
Cloud-Based Production Tools
The shift to cloud-based production tools makes live streaming and remote live production more efficient and scalable.
These tools enable:
- Real-time collaboration, allowing teams to work together from anywhere in the world.
- Instant access to production assets, eliminating the need for on-site infrastructure.
- Scalable computing power, adjusting resources based on streaming demand.
- Seamless integration with existing broadcast systems for enhanced workflows.
- Virtual production capabilities to enable remote talent and AI-driven graphics insertion.
- AI-powered automation tools, optimizing live production, camera switching, and content tagging.
4 Benefits of Remote Broadcasting
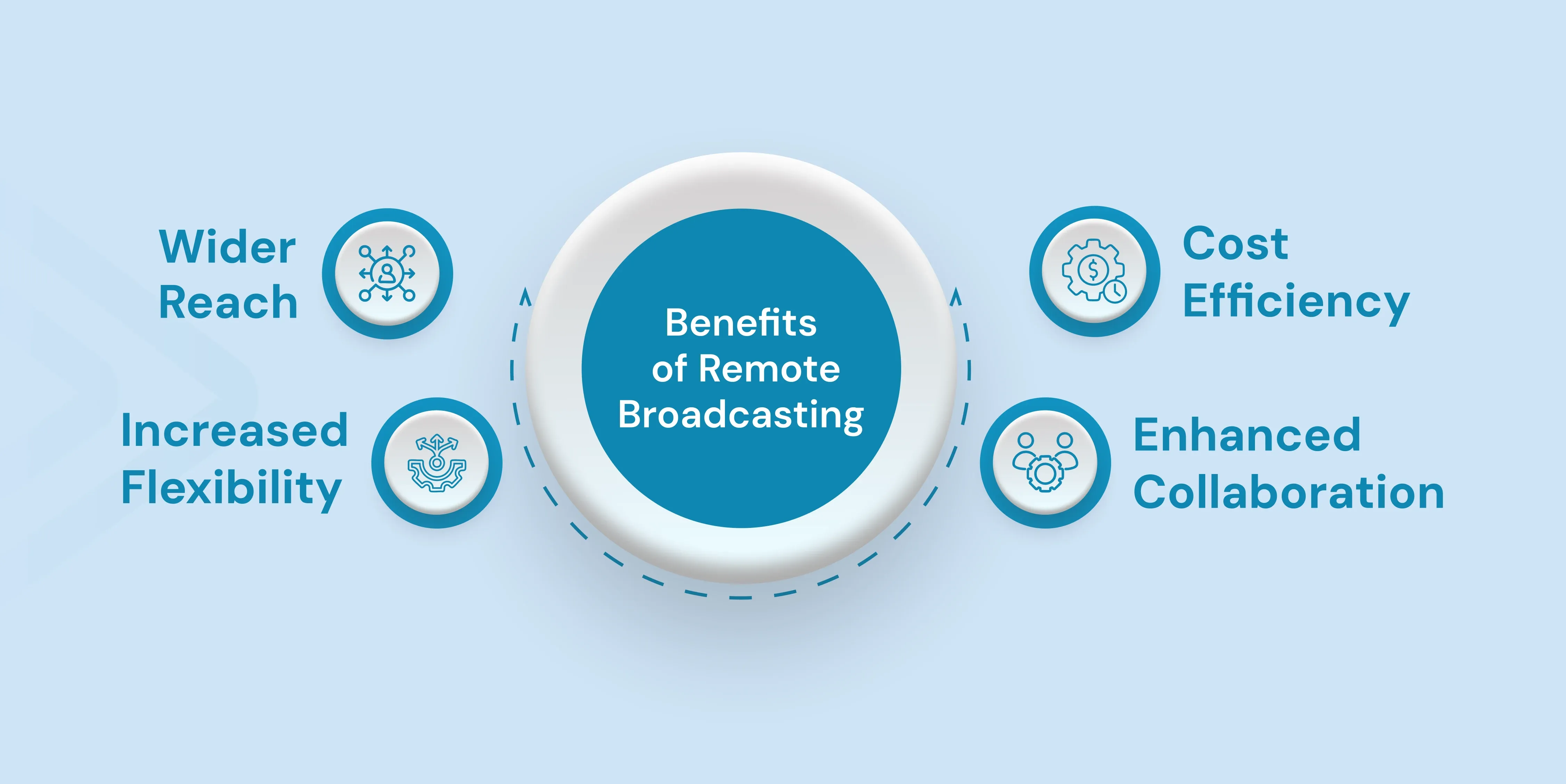
1. Cost Efficiency
Live streaming from a remote location significantly reduces operational expenses. It eliminates the need for expensive satellite trucks, drastically reducing equipment transportation costs and requiring far fewer on-site staff.
Remote broadcasting decreases facility rental expenses, optimizes resource allocation across multiple productions, and reduces travel and accommodation costs, further contributing to a more budget-friendly approach.
2. Increased Flexibility
Content creators gain unprecedented flexibility in their production approaches. Location-independent broadcasting capabilities mean you can stream from virtually anywhere with a reliable internet connection.
Need to change your production on the fly? Remote broadcasting allows for quick adaptation to changing requirements and seamless integration with existing workflow systems.
3. Wider Reach
OTT platform integration enables broadcasters to effectively reach global audiences. Access to international markets without traditional distribution constraints opens up new revenue streams and expands viewership.
Plus, multi-device content delivery makes for a consistent viewing experience, whether your audience is watching on a smartphone, tablet, smart TV, or computer.
Customized viewing experiences and enhanced audience targeting capabilities improve engagement, while real-time analytics and viewer insights provide valuable data to understand audience preferences.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
Real-time communication tools and platforms connect teams regardless of location. Shared access to production assets and resources streamlines workflows, which enhances productivity.
Best Practices for Remote Broadcasting
Successful remote broadcasting requires a systematic approach encompassing technical setup, rigorous quality control, and strategies for maximizing audience engagement. These best practices are essential for ensuring reliable and professional broadcasts while maintaining viewer satisfaction.
Network Optimization
Reliable internet connectivity is the very foundation of successful remote broadcasting. It's the lifeblood of your live streaming website or platform. So, can you stream without internet? The simple answer is no—a stable internet connection is absolutely crucial.
To ensure seamless live streams, prioritize high-bandwidth connections, ideally with redundant paths and Quality of Service (QoS) configurations to give priority to broadcast traffic. Think of it like having a dedicated express lane for your video stream.
Implement robust backup solutions, perhaps using a combination of fiber, cellular, and satellite technologies from different providers, to ensure continuity even if your primary connection falters.
Real-time network monitoring tools are also essential for proactively identifying and addressing any potential issues before they impact viewers. These tools should track key metrics like latency, packet loss, and jitter, providing you with a clear picture of your network's health.
Even mobile hotspots or alternative internet connections can be used to stream without wifi. For mission-critical broadcasts, redundant and diverse internet connections are not just recommended—they're essential.
Quality Control
Maintaining consistent, high-quality broadcasts requires systematic monitoring and control measures. Pre-broadcast testing is absolutely vital. Establish thorough testing procedures to verify all systems, including encoder settings, network conditions, and backup systems, before you go live. This is your opportunity to identify any potential issues and ensure everything is functioning as expected.
Live monitoring during the broadcast is equally important. Implement continuous monitoring of both audio and video quality, using automated systems that can detect and alert operators to any potential issues before they impact the viewer experience.
Don't wait for viewers to complain—be proactive. Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) like viewer engagement, buffer ratio, and playback failures provides valuable data for maintaining and continually improving broadcast quality over time.
Security Measures
Protecting your valuable content and ensuring secure transmission requires robust security protocols. Encryption is paramount here. Implement enterprise-grade encryption for content during transmission and storage, using industry-standard protocols.
Authentication is another key aspect of secure video streaming. Deploy multi-factor authentication systems to ensure only authorized personnel can access your broadcasting systems and controls. This adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Staying up-to-date is also essential. Maintain systematic security updates and conduct regular protocol reviews to protect against emerging threats and ensure compliance with industry best practices.
Audience Engagement
Interactive features, such as live chat, polls, and Q&A sessions, encourage viewers to become active participants rather than passive observers. These features create a more immersive and dynamic experience, making viewers feel like they are part of the broadcast.
Real-time monitoring of viewer feedback is invaluable. Establish systems to gauge audience response and adjust content accordingly. This allows you to adapt to viewer preferences and keep them engaged.
Providing multiple viewing quality options is crucial for ensuring accessibility across different devices and internet connections. This, combined with adaptive streaming technologies, ensures that viewers can enjoy a high-quality experience regardless of their individual circumstances.
How inoRain Ensures Remote Broadcasting Success
inoRain's OTT solutions transform traditional broadcasting approaches into powerful, flexible remote broadcasting capabilities. Our platform you can use cutting-edge technologies with user-friendly interfaces to ensure successful remote broadcasting.
With inoRain, You Can Have
Advanced Streaming Features: Multi-bitrate encoding systems, real-time analytics insights, and performance metrics
Robust Security: Multi-DRM protection, enterprise-grade encryption, and secure content storage.
Simplified Management: OTT solutions with a centralized dashboard that provides complete control over all aspects of content delivery, from scheduling to monitoring.
Flexible Monetization: Various monetization models including SVOD, AVOD, TVOD, HVOD, FAST, and more
Get the OTT platform that scales as you grow.
Conclusion
Remote broadcasting has revolutionized live streaming on OTT platforms, breaking down traditional barriers and opening up endless possibilities for content creators and broadcasters. As technology advances and audience expectations shift, this transformation will only accelerate, making remote live streaming, cloud-based production, and AI-driven automation the new industry standard.
inoRain is at the forefront of this evolution, providing powerful remote broadcasting solutions designed to help you stream smarter, reach wider, and grow faster.
Ready to take your live streaming to the next level? Contact our experts for a personalized demo and discover how you can use our OTT solutions to manage, monetize, and transform your content like never before.
Frequently Asked Questions
Founder / CEO
Andranik is the CEO and Co-Founder of inoRain OTT and the Co-Founder of HotelSmarters, specializing in next-generation streaming technologies and digital transformation for the hospitality sector. He focuses on building innovative, scalable solutions for video delivery, OTT monetization, and data-driven hospitality management. His work bridges technical sophistication with practical business impact, helping organizations modernize their digital ecosystems and improve operational efficiency.

What is OTT? Benefits and 5 Types of OTT Services
This article has all the answers to what is an OTT platform, how OTT works and the different types of OTT services

What is OTT Analytics? Key Metrics And Tools
In this article, we uncover what OTT analytics is, the top metrics and tools required to keep your OTT platform ahead of the curve - and the competition.

What is SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand)? 2026 Guide
What is SVOD, how does it work, and why are businesses turning to SVOD platforms to create new revenue streams? This article has all the answers.
