
AES Video Encryption: Benefits And Implementation
You’ve already spent days and nights curating high-quality videos, and your subscriber count is climbing the graph. But then, you notice that your revenue isn’t reflecting the value of your work, only to find out that unauthorized sites have streamed your content.
To be on the safe side, many OTT platforms are now using AES video encryption. This highly secure standard safeguards video content from unauthorized access.
This article will explain the intricacies of AES video encryption, its working principles, use cases, benefits, and implementation in OTT and IPTV platforms.
Key Takeaways
- AES video encryption is a highly secure encryption standard that safeguards video content from unauthorized access.
- The process of AES encryption comprises the steps of key expansion, substitution, shifting, and mixing to give an encrypted ciphertext at the end.
- HBO’s case study is an example of why AES video encryption is crucial to combating cyber breaches and data theft.
- AES integration reduces man-in-the-middle attacks, supports both software and hardware solutions, and comes with extended encrypted keys. It offers better control over content access, making it a top-notch security protocol altogether.
What is AES Video Encryption?
AES video encryption is a highly secure encryption standard that safeguards video content from unauthorized access. It works by converting video data into an unreadable format that only authorized users can access with the correct decryption keys
AES stands for Advanced Encryption Standard. AES encryption is a cryptographic technique developed in 2001 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology to shield digital content through advanced encryption methodologies.
AES itself is known as one of the most secure encryption algorithms available. It uses symmetric key encryption, and the same key is used for both encryption and decryption.
The only one who has access to that “cryptographic key” can decrypt the video data. In terms of video content protection, AES encrypts video data into complex ciphers that any unauthorized party can’t access. Even authorized access to the video is managed by a secure infrastructure.
How Does AES Encryption Work?
AES encryption secures video content by converting it into ciphertext using a systematic and multi-step process. To understand what exactly happens during the encryption process, here are its general steps:
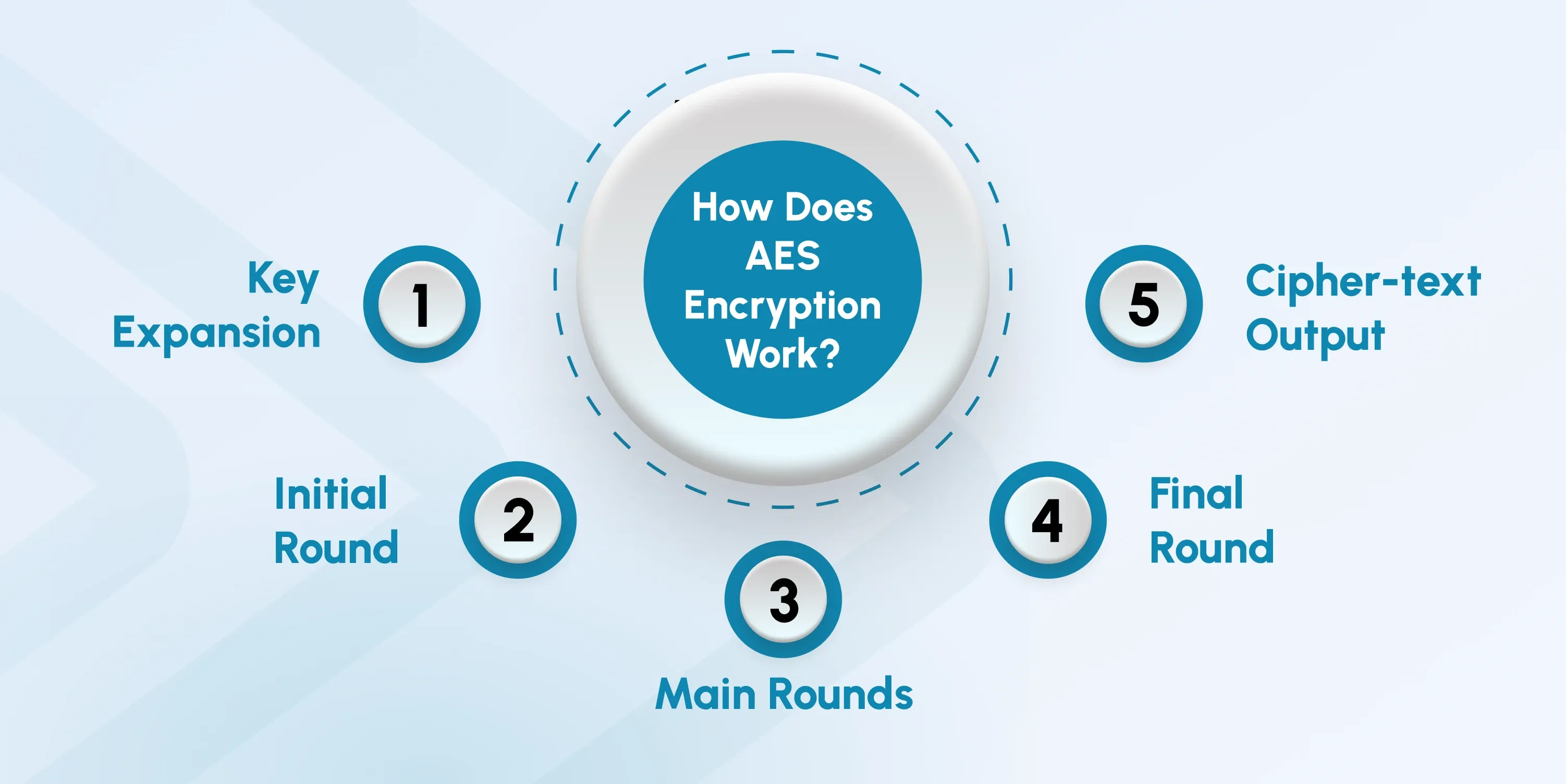 Step 1: On ingest servers, an AES algorithm scrambles the raw video data.
Step 1: On ingest servers, an AES algorithm scrambles the raw video data.
Step 2: The encrypted video is then sent to a content delivery network (CDN).
Step 3: It stays encrypted on CDN nodes until it reaches the end user’s device.
Step 4: Once the encrypted video reaches the end user, the correct AES key decrypts the video, so the scrambled data is watchable again.
Now, for a deeper understanding of how AES encryption works, here's a detailed technical breakdown:
The AES encryption process consists of several well-defined steps:
1. Key Expansion
For advanced protection, the original encryption key undergoes a process called key expansion, generating multiple round keys. The number of rounds depends on the key size:
- 10 rounds for 128-bit keys.
- 12 rounds for 192-bit keys.
- 14 rounds for 256-bit keys.
These round keys are used throughout the encryption process to add layers of security.
For advanced protection, the original encryption key undergoes a process called key expansion. In this process, a series of round keys is generated from the original key, and their quantity depends on the size of the original key used:
- 10 rounds for 128-bit keys
- 12 rounds for 192-bit keys
- 14 rounds for 256-bit keys
2. Initial Round
The process of encryption begins with an initial round that involves a single operation:
- AddRoundKey: Here, a bitwise XOR operation is used to combine the data block with the first round key.
3. Main Rounds
After combining the data blocks of video with the first round key, a series of main rounds are performed, each consisting of four primary types of transformation:
- SubBytes: Each byte in the data block is replaced with a corresponding byte from a fixed substitution table known as the S-box. This step provides non-linearity in the encryption process.
- ShiftRows: The rows of the data block are shifted cyclically to the left. Each row is shifted by a different number of bytes, which contributes to the data diffusion.
- MixColumns: Each column of the data block is treated as a polynomial, and the columns are mixed to provide additional diffusion. This transformation combines the data in a way that makes it more resistant to cryptanalysis.
- AddRoundKey: Another round key is combined with the data block using a bitwise XOR operation.
This sequence of transformation is repeated for a specified number of rounds, which completely depends on the key length.
4. Final Round
The final round omits the MixColumns step and consists of only three types of transformation:
- SubBytes
- ShiftRows
- AddRoundKey
5. Ciphertext Output
After the completion of all rounds, the result is the ciphertext—a securely encrypted version of the original plaintext data.
AES Decryption
Consider the decryption process as the reverse of the encryption process. Now, the ciphertext uses the round keys generated during key expansion and goes through a series of rounds, but in reverse order. The same steps are applied, but now the series will be:
- AddRoundKey
- Inverse MixColumns
- Inverse ShiftRows
- Inverse SubBytes
Benefits of AES Video Encryption for Content Providers
Mitigates Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
In such attacks, where hackers intercept and manipulate data exchanged between users and content providers, implementing AES video encryption is a great help. This is because it makes sure that even if the data is intercepted during transmission, it remains in its encrypted form.
Supports Both Hardware and Software Solutions
Another benefit of AES video encryption is the versatility it brings to content providers. Unlike other video streaming software options, it adds a security layer to the video content on both hardware and software levels.
Extended Key Lengths for Better Security
AES encryption supports key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits, giving content providers a choice to select the security level they want. With correct AES key management, the level of security will be unmatched.
Improved Control Over Content Access
Encrypting content with AES provides better control over who can access it. Providers can easily manage and restrict access by using unique encryption keys for different users or sessions. This is also beneficial for content monetization.
Why Use AES For Video Encryption?
 As people are now more into digital streaming networks, the frequency of cybercrimes has also surged, which is a risk to their reputation and finances. Cybersecurity Ventures’ 2021 report highlighted that global cybercrime costs will hit $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
As people are now more into digital streaming networks, the frequency of cybercrimes has also surged, which is a risk to their reputation and finances. Cybersecurity Ventures’ 2021 report highlighted that global cybercrime costs will hit $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
Furthermore, the Identity Theft Resource Center reported that the number of data breaches in the U.S. increased by 68% in 2021, and the common reason behind many was unauthorized access to sensitive content, including video data.
Ponemon Institute also carried out a survey, which revealed that 67% of organizations that experienced a data breach did not encrypt their sensitive data. Together, these statistics highlight the importance of video encryption.
However, refer to HBO’s case study to understand why to use AES in particular for video encryption, and its effectiveness in combating data breaches.
Back in 2017, hackers accessed the proprietary data of HBO and published the unreleased episodes of a popular show. To avoid any such future breaches, HBO implemented various security measures, including AES video encryption for encrypted video streaming. By encrypting their data, HBO could protect sensitive information and restrict access to only authorized users.
So, the implementation of this security protocol by giants like HBO underscores the effectiveness of AES video encryption.
AES Encryption in OTT and IPTV
On OTT platforms, AES encryption secures digital content streamed over the internet, including browsers and applications. It simply segments the video data into small chunks and encrypts those chunks with a unique or shared key, depending on the in-place security architecture.
When a user requests to watch a video, the OTT service decrypts the content on the server side, making it accessible only to authorized users.
With an IPTV system, the AES encrypts live and on-demand videos before they are sent over the broadband connection, converting ordinary video into encrypted video. The entire encryption process is done in real-time, and decryption is performed simultaneously via a set-top box or application provided by the IPTV service provider.
Implementation of AES Encryption in OTT and IPTV Platforms
 For better security and integrity of video content on OTT (Over-the-Top) and IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) platforms, integrating AES encryption is essential. Apart from protecting the data from unauthorized access, this implementation also enhances user trust in digital content delivery services.
For better security and integrity of video content on OTT (Over-the-Top) and IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) platforms, integrating AES encryption is essential. Apart from protecting the data from unauthorized access, this implementation also enhances user trust in digital content delivery services.
To effectively implement AES encryption, the first step is to select the correct key management strategy.
Key management is critical in AES encryption, as the security of the encrypted content relies heavily on how encryption keys are generated, distributed, and stored.
Content providers must ensure that these keys are securely stored and accessible only to authorized users. Many OTT and IPTV platforms use secure servers and protocols, such as HTTPS, to safeguard these keys during transmission.
Next comes the step of content segmentation in the implementation process. Video content is often broken down into smaller segments, each of which can be encrypted separately. This method improves security and optimizes streaming performance, allowing users to experience high-quality playback without delays.
So, whether it's a company or a content provider, an encrypted video player is a must to ensure the safety of digital property.
inoRain is an OTT solutions provider that allows content providers to stream their content securely by offering integrated AES video stream encryption. We’ll help you reach audiences across multiple devices and browsers, maintaining high-quality content, without any risks of data breaches.
Challenges and Limitations of AES Encryption
Computational Demand and Latency
As the key sizes in AES encryption are longer (such as 256 bits), the process of video encryption is computationally intensive. This can create delays in video playback when implemented in video encryption software or when decrypting videos for access. The high equipment demands of AES video encryption may affect real-time streaming, especially on lower-end devices or those already handling high-quality video files.
Potential Side-Channel Attacks
While AES encryption is highly secure against brute-force attempts, it can still be vulnerable to side-channel attacks, where hackers exploit data from the physical implementation of encryption, such as timing and power consumption.
Hardware-based AES video intercom systems are especially susceptible to these risks, where physical access could expose sensitive information.
Impact on Streaming Quality
Speed and quality can both be affected by implementing AES encryption on content distributed via OTT or IPTV platforms. Viewers might experience delays or reduced quality as the content has to undergo complex layers of encryption and decryption, particularly if the encryption software or intercom system doesn't seamlessly integrate with streaming protocols.
Implementation Costs and Complexity
For smaller content providers or new businesses, the cost of implementing AES encryption on OTT or IPTV platforms can be significant. Ongoing maintenance, regular updates, and real-time monitoring further add to these costs, especially if the content is delivered globally with specific compliance needs.
Conclusion
Despite AES video encryption shielding the content by adding extra layers of security, it’s crucial to continue monitoring and checking for updates to maintain security over time.
Remember, cyber threats are evolving daily, so the need to be more vigilant regarding security measures is becoming intense. For this reason, content providers must be equipped with all the basics, from learning how to encrypt a video to knowing the encryption models, so that they remain one step ahead of potential breaches.
Ready to safeguard your OTT platform? inoRain offers advanced solutions equipped with AES encryption to ensure your content remains secure. With our expertise in video protection and streaming technology, you can deliver premium experiences while staying ahead of cyber risks.
Partner with inoRain today to elevate your platform’s security.
FAQs
What is AES Encryption?
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a symmetric block cipher that encrypts data in 128-bit blocks using keys of 128, 192, or 256 bits. It is widely adopted to secure sensitive information across various digital platforms.
How secure is AES-128 encryption?
AES-128 encryption is known as highly secure for most applications. It's the shortest key length among AES variants, but remains robust against known cryptographic and brute-force attacks.
Is AES-256 encryption better than AES-128?
AES-256 encryption has a longer key length than AES-128, so it provides a stronger protection against brute-force attacks. However, the decrypting process is slower with AES-256 due to its complex structure.
AES-128 is more efficient because the key is shorter, resulting in a faster decryption process.
Both encryption standards are highly secure. The choice between them depends on the user’s specific security needs, devices, and performance considerations.
Co-founder / CTO
Armen is the CTO and Co-Founder of inoRain OTT and Co-Founder of HotelSmarters, specializing in advanced streaming technologies, OTT strategy, and interactive TV systems. He builds scalable end-to-end video delivery solutions and drives technical innovation across hospitality and streaming platforms, bridging complex engineering with practical business impact.

What is OTT? Benefits and 5 Types of OTT Services
This article has all the answers to what is an OTT platform, how OTT works and the different types of OTT services

What is OTT Analytics? Key Metrics And Tools
In this article, we uncover what OTT analytics is, the top metrics and tools required to keep your OTT platform ahead of the curve - and the competition.

What is SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand)? 2026 Guide
What is SVOD, how does it work, and why are businesses turning to SVOD platforms to create new revenue streams? This article has all the answers.
