
The Best Audio Bitrate for Your Streaming: How to Choose
Audio bitrate quality can either capture your audience’s attention or lose them entirely.
But what is audio bitrate? How do you find the sweet spot between great-sounding audio and the practical limits of bandwidth or file sizes?
This article answers all of these questions and more.
We discuss the impact of audio bitrate on streaming and provide all the details you need to make informed decisions based on your content and audience.

Key Takeaways
- The audio bitrate is the most important factor in determining the quality and performance of your stream.
- Higher bitrates equate to better quality but use more bandwidth, resulting in buffering on slower connections.
- Different types of content used in music, podcasts, and livestreams all have different sweet spot bitrates.
- Newer compression formats, such as AAC, have better sound quality at lower bitrates than older formats like MP3.
- Adaptive bitrate streaming will seamlessly switch between streams, so users get the best audio bitrate for streaming based on their internet speed.
What is Audio Bitrate?
Audio bitrate refers to the amount of data per second that an audio file or stream processes and is usually measured in kilobits per second (kbps). In simpler terms, it represents how much information is packed into each second of audio playback or recording.
So, is a higher audio bitrate better?
Yes! Higher bitrates capture more detail, resulting in better audio quality. For example, 320 kbps delivers richer, more vivid sound than 128 kbps, making it ideal for music enthusiasts. However, higher bitrates also demand more bandwidth and storage space, which can impact streaming performance and file management.
 For content creators or producers, bitrate is a critical factor because it directly affects their audience’s experience with their material. Whether someone is listening on high-end speakers or budget-friendly headphones, the chosen bitrate influences the clarity, accessibility, and overall enjoyment of the audio.
For content creators or producers, bitrate is a critical factor because it directly affects their audience’s experience with their material. Whether someone is listening on high-end speakers or budget-friendly headphones, the chosen bitrate influences the clarity, accessibility, and overall enjoyment of the audio.
Balancing quality and practicality is key, ensuring the content sounds great while remaining efficient for different devices and platforms.
How Bitrate Affects Audio Quality
The audio bitrate for streaming is essential in determining the quality of audio in streams or files. In general, a higher bitrate means more detailed audio, resulting in richer, clearer sound. This is particularly important for music streams, where subtle tonal shifts and the nuances of instruments are paramount to the listening experience.
However, lower bitrates, while saving bandwidth and file size, can compromise sound quality. At lower bitrates, listeners may notice muffled audio, distortion, or a lack of depth in the sound. This tradeoff is especially noticeable in complex audio like music, where clarity is key.
That said, higher bitrates are not always better. The "ideal" bitrate depends on your content and audience. For example:
- Speech-focused content like podcasts delivers excellent clarity at lower bitrates (96–128 kbps).
- Music streams, on the other hand, typically require 192–320 kbps to maintain optimal quality.
It’s also important to consider internet speed and playback devices. Higher bitrates demand faster connections and better hardware, which might limit accessibility for some listeners.
Finding the right balance between bitrate, audio quality, and resource efficiency is essential. The goal is to deliver a pleasant listening experience that satisfies your audience's expectations without overwhelming their streaming devices or your streaming capabilities.
Factors Affecting Audio Bitrate Selection
Choosing the best audio bitrate for streaming is not about trying to reach the highest quality. Instead, it’s about getting the perfect balance for your content, audience, and technical setup. A variety of factors come into play when deciding what works best for you.
Below are the top five key considerations.
Type of Content
Various kinds of content bear different levels of detail in the audio. Where music streams require higher bitrates to give richness to the sound, speech-only content, such as podcasts, can work at far lower bitrates with little apparent loss.
Available Bandwidth
The internet speed of your audience dictates the maximum bitrate they can handle without buffering. A bitrate that’s higher than the bandwidth will result in dropped audio or lagging streams.
Target Audience and Devices
Listeners using high-end audio equipment may demand higher bitrates for better audio quality, while casual users with basic headphones may not.
Requirements by the Streaming Platform
Different streaming platforms, such as YouTube, Twitch, or Spotify, have bitrate recommendations or upper limits. Sticking within those bounds provides maximum compatibility without possible technical glitches.
Compression Format
The best audio codecs, like Advanced Audio Coding (AAC), offer better quality at lower bitrates than older formats like MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3, known as MP3.
Live vs. On-Demand Content
Live streaming requires lower bitrates to reduce latency, while on-demand content can leverage higher bitrates for better quality.
Recommended Audio Bitrates for Streaming
What is a good audio bitrate for streaming?
The ideal bitrate depends on several factors, including the content type, platform, and audience. Bitrates can vary widely, with higher bitrates offering better quality but requiring more bandwidth. Finding the right balance is essential to ensure smooth streaming and great sound.
Let’s see what bitrates work the best for different needs.
For Music Streaming
- Standard Quality: 128 kbps (MP3)
- High Quality: 192–256 kbps (AAC)
- Lossless Quality: 320 kbps or higher (Free Lossless Audio Codec or FLAC)
In the case of music, a high-quality audio bitrate for streaming is the focus. The music streams should be of high quality to capture the full depth and richness of the sound. Anything from 192 to 320 kbps would be great for Spotify or YouTube Music so that playback remains crystal clear with no noticeable compression artifacts.
This offers a good balance between audio quality and bandwidth efficiency, making it suitable for both casual listeners and audiophiles.
For Video Streaming
- Standard Definition Resolution or SD (480p): 96–128 kbps
- High Definition Resolution or HD (720p and 1080p): 128–192 kbps
- 4K Resolution: 192–320 kbps
Video streaming is more about complementing the video with synchronized, clear audio. Most platforms recommend speech-heavy content like vlogs or tutorials stick within the range of 128–192 kbps.
In comparison, action-packed or cinematic videos often benefit from higher audio bitrates, around 192 kbps or more, to enhance the immersive experience. Richer soundscapes, like explosions, background music, or detailed effects, are better represented at higher bitrates.
For Live Streaming
- Low Bandwidth: 64–96 kbps
- Standard Bandwidth: 128 kbps
- High Bandwidth: 192 kbps
In live events, maintaining a consistent audio bitrate for streaming is critical to ensuring smooth playback and avoiding interruptions. The appropriate bitrate largely depends on the type of content being streamed.
For voice-heavy streams, a bitrate of 96–128 kbps is typically sufficient. These formats prioritize intelligibility over intricate sound details, so lower bitrates work well without sacrificing clarity.
For live music performances or high-energy gaming streams, richer audio is required to capture dynamic sounds and ambiance. Bitrates up to 192 kbps are often recommended to enhance the listening experience for viewers.
Consistency in bitrate is especially important during live streams, as fluctuations can cause buffering or quality drops for your audience.
For Podcasts and Voice Content
When creating podcasts or voice-heavy content, the bitrate you choose affects clarity, file size, and accessibility. Here are the common recommendations based on channel type:
- Mono Audio: 64–96 kbps works well for clear, speech-focused content like solo podcasts or audiobooks. Mono audio uses only one channel, requiring less data while maintaining intelligibility.
- Stereo Audio: 128 kbps is ideal for podcasts, audiobooks, or content with multiple voices, sound effects, or music. Stereo adds depth by using two channels, which serve to improve the listening experience.
For recording, a bitrate of 192 kbps or higher is often recommended. This captures richer sound details, which is especially useful for editing and preserving quality across different platforms.
Compression Formats and Their Roles in Bitrate
What is an audio codec, and how does it affect your streaming quality?
An audio codec determines how your audio is encoded, compressed, stored, and transmitted. It significantly impacts the bitrate required for streaming and the overall quality of your content. Choosing a suitable codec and format is key to delivering high-quality audio while optimizing bandwidth and storage.
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer III)
The MP3 format is widely supported across devices and platforms, making it a popular choice for compatibility. However, it’s less efficient, requiring higher bitrates to maintain quality. For example, a 128 kbps MP3 may sound inferior to a 96 kbps AAC file.
AAC (Advanced Audio Codec)
AAC is more efficient than MP3, offering better audio quality at lower bitrates. For example, AAC at 128 kbps delivers near-CD quality, making it ideal for bandwidth-sensitive applications like live streaming.
Compression formats have been broadly classified into lossy and lossless formats. Lossy formats, which include MP3 and AAC, compress a file to a smaller size by getting rid of audio data less noticeable to the human ear and are more suitable for streaming, where bandwidth efficiency is key.
The disadvantage with this is that sometimes one has to suffer the loss of audio fidelity with decreased bitrates. As such, AAC may not offer the best bitrate for streaming live events, such as music shows or concerts.
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
FLAC is a popular lossless format that compresses audio without quality loss. It's open-source and highly efficient, but like ALAC, it produces larger files. FLAC is platform-agnostic, making it versatile for high-quality streaming. It provides the best bitrate for streaming audiophile-grade content or archival content where quality cannot be compromised.
ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec)
ALAC is a lossless format designed by Apple. As one of the best audio codecs, it retains the original audio quality without compression-related losses, making it ideal for high-fidelity music streaming. However, ALAC results in larger file sizes, which can be a drawback for limited bandwidth environments.
Lossless formats such as FLAC and ALAC retain all audio data, and therefore the original quality, but require much larger bitrates and storage in exchange. The kind of compression format used influences the experience of your audience with your content.
Indeed, it’s possible to get near-CD quality with AAC at 192 kbps or a similar higher-quality lossy format that keeps file sizes manageable. In contrast, going lossless might be more for the real audiophiles but could demand higher bandwidth, which isn’t always practical for all users.
Knowing the trade-offs in compression format and bitrate is important to optimize your streams for both quality and accessibility as a creator.
Opus
Opus is a modern codec optimized for internet streaming services. It delivers excellent quality at extremely low bitrates, making it ideal for live streaming and bandwidth-limited scenarios.
Opus supports variable bitrates and dynamic adaptation, ensuring consistent quality.
Comparison of Formats by Use Case
When choosing a compression format, consider factors such as your target audience, platform compatibility, and the desired audio quality in relation to bandwidth constraints.
Formats like AAC and Opus strike a balance between quality and efficiency, while ALAC and FLAC cater to audiophiles who prioritize lossless sound reproduction.
| Format | Compression Type | Efficiency | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP3 | Lossy | Moderate | Widely supported but less efficient. Requires higher bitrates to maintain quality. |
| AAC | Lossy | High | More efficient than MP3, offering better quality at lower bitrates. Used for music/video streaming with bandwidth limits. |
| ALAC | Lossless | Low | High-fidelity audio in Apple ecosystems. |
| FLAC | Lossless | Low | Audiophile-grade music streaming. Preserves original quality but results in larger file sizes. |
| Opus | Lossy | Very High | Designed for live streaming, video conferencing, and real-time communications, it offers high quality at remarkably low bitrates. |
5 Steps to Determine the Best Audio Bitrate for Your Needs
Consider your specific streaming needs and your audience's preferences to make an informed decision.
Here's how you can determine the best audio bitrate for your needs:
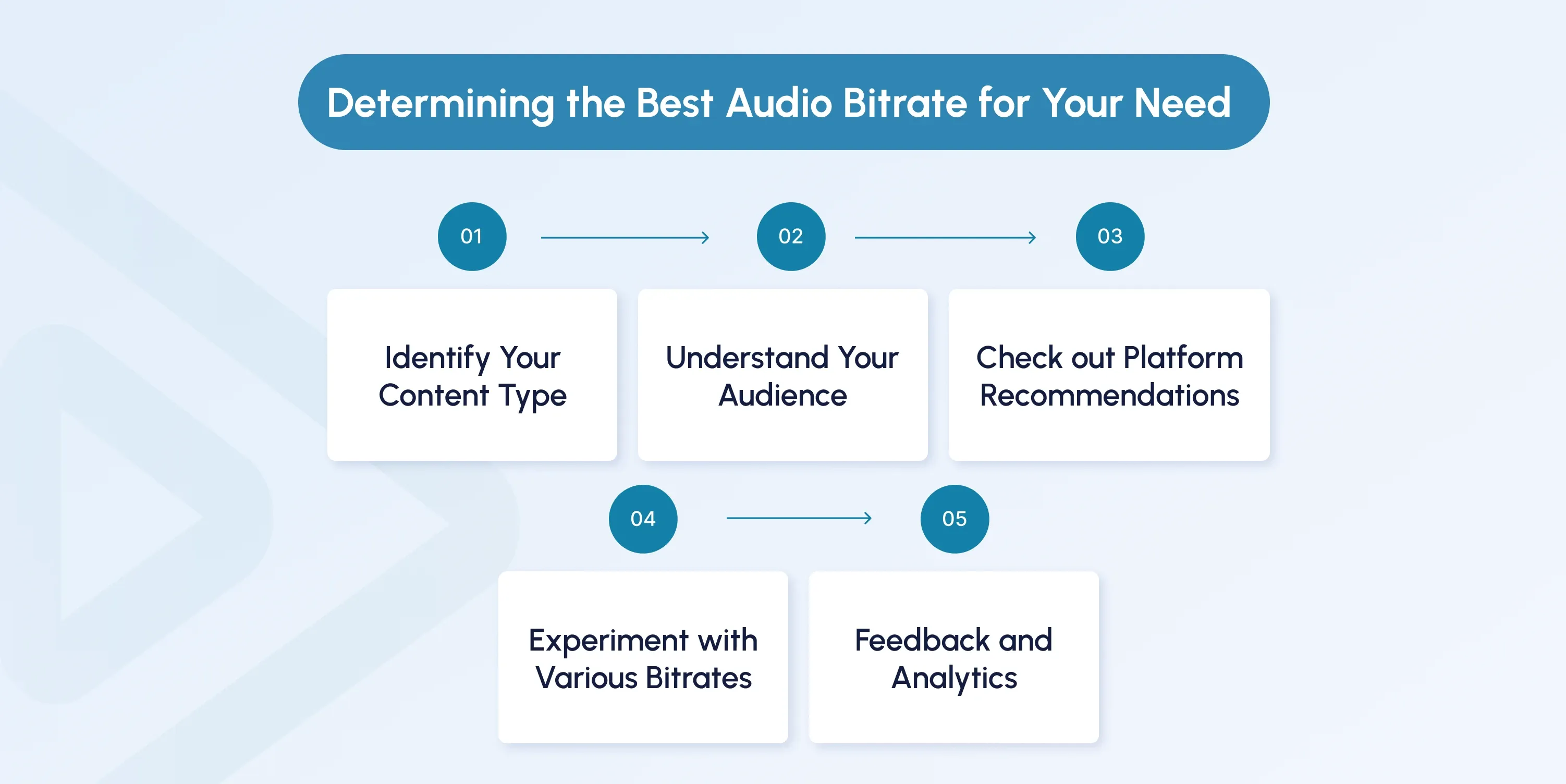
Step 1: Identify Your Content Type
What are you streaming? Music, podcasts, live video, or gaming? Each content type has its own bitrate requirements. Typically, higher bitrates are ideal for music, while lower bitrates work for voice content.
Step 2: Understand Your Audience
Consider your audience's internet speed and usual playback devices to ensure your stream stays accessible without buffering or quality loss.
Step 3: Check out Platform Recommendations
When streaming, it’s essential to adhere to the bitrate guidelines provided by your platform. Platforms like YouTube, Twitch, and Spotify often offer specific recommendations based on content type (e.g., music, gaming, or podcasts) to ensure consistent quality across different devices and networks.
Step 4: Experiment with Various Bitrates
Take the time to experiment with different bitrates to find the ideal balance between audio quality and bandwidth usage. Start with platform-recommended settings as a baseline. You can then gradually test higher or lower bitrates to identify what works best for your content type.
The goal is to strike a balance between delivering great sound quality and keeping your streams practical for diverse internet speeds and devices.
Step 5: Feedback and Analytics
Pay heed to audience feedback and platform analytics to see if your chosen bitrate meets their expectations or needs some adjustment. Use this data to adjust your bitrate or codec choices for better alignment with your audience’s expectations.
Challenges in Audio Bitrate Selection
Choosing the right audio bitrate isn’t as simple as it seems. Several factors can make the decision a tad complicated. Maintaining a balance of quality, accessibility, and technical limitations requires careful consideration.

Challenges in audio bitrate selection
Below are some common challenges you might face when selecting the best audio bitrate for streaming:
Balancing Quality and Bandwidth
The higher the quality, the higher the bitrate, and hence the greater the consumption of bandwidth, that may cause buffering issues in users with low bandwidths. On the other hand, lower bitrates reduce file sizes and improve streaming stability but may compromise audio clarity and richness.
Platform Limitations
Different types of content demand varying bitrates. For example, speech-heavy content (podcasts, audiobooks) can maintain clarity at lower bitrates (96–128 kbps). Music or cinematic content requires higher bitrates (192–320 kbps) to capture the complexity of sounds.
Choosing the wrong bitrate for your content can result in either wasted resources or diminished audio quality.
Diverse Needs of Viewers
Audiences use a variety of devices (e.g., high-end speakers, basic headphones) and internet speeds, making it difficult to meet everyone’s expectations. Your chosen audio bitrate for streaming must cater to both high-fidelity users and those in bandwidth-constrained environments.
File Size Concerns and Platform Limitations
Higher bitrates also equate to larger file sizes, which can prove challenging when trying to store or upload this content. Streaming platforms often impose maximum bitrate limits, and exceeding these can lead to re-encoding, which may degrade audio quality. Some platforms recommend specific codecs and bitrates, further narrowing your options.
Technical Limitations
Higher bitrates demand more storage and processing power, which can strain your equipment during recording, editing, or live streaming. Lossless formats, while offering top-tier quality, may not be practical for creators with limited resources.
Start Effective Streaming with inoRain’s Solutions
 inoRain offers innovative OTT solutions tailored to optimize streaming for content creators, telecom operators, and other streaming industries. With a focus on reliability, scalability, and advanced technology, we enable you to deliver high-quality streaming experiences that cater to your target audience’s needs.
inoRain offers innovative OTT solutions tailored to optimize streaming for content creators, telecom operators, and other streaming industries. With a focus on reliability, scalability, and advanced technology, we enable you to deliver high-quality streaming experiences that cater to your target audience’s needs.
Here’s what we have to offer for your streaming business growth:
- A Customizable OTT Platform
- Advanced Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- 10+ Monetization options
- Analytics and insights
- Security and compliance (integrated strong DRM)
- Scalable and reliable architecture
A partnership with inoRain guarantees you access to tailored solutions, innovative technology, and global reach.
Get Your White-Label OTT Platform Here
Conclusion
The correct audio bitrate for streaming is essential for delivering a high-quality experience. To make the right choice, consider the nature of your content, your audience’s expectations, and your platform’s limitations.
By balancing these factors, you can find the sweet spot between great sound quality and efficient performance. Understanding the best audio bitrate for streaming your content ensures your audience enjoys the best experience without technical hiccups.
Whether you’re streaming music, live gameplay, or podcasts, bitrate decisions play a vital role in seamless delivery.
FAQs
What is audio bitrate?
Audio bitrate is the amount of data processed per unit of time in an audio file, measured in kilobits per second (kbps). A higher bitrate generally indicates better audio quality, as more data is used to represent the sound. However, higher bitrates also result in larger file sizes and increased bandwidth requirements.
How does audio bitrate affect live streaming quality?
Audio bitrate determines the clarity of the sound during live streaming. Higher bitrates provide better quality but require more bandwidth, which can lead to buffering if the audience's internet connection is slow.
How can I balance audio quality and bandwidth efficiency?
Choose modern codecs like AAC or Opus that offer superior quality at lower bitrates. Test different configurations and monitor audience feedback to find the best balance.
How does adaptive bitrate streaming improve audio quality?
Adaptive bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts the bitrate based on the user's internet speed, ensuring the best possible quality without interruptions.
Which compression format is better for streaming: MP3 or AAC?
AAC is generally better for streaming as it provides higher quality at lower bitrates compared to MP3, making it more bandwidth-efficient.
Co-founder / CTO
Armen is the CTO and Co-Founder of inoRain OTT and Co-Founder of HotelSmarters, specializing in advanced streaming technologies, OTT strategy, and interactive TV systems. He builds scalable end-to-end video delivery solutions and drives technical innovation across hospitality and streaming platforms, bridging complex engineering with practical business impact.

What is OTT? Benefits and 5 Types of OTT Services
This article has all the answers to what is an OTT platform, how OTT works and the different types of OTT services

What is OTT Analytics? Key Metrics And Tools
In this article, we uncover what OTT analytics is, the top metrics and tools required to keep your OTT platform ahead of the curve - and the competition.

What is SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand)? 2026 Guide
What is SVOD, how does it work, and why are businesses turning to SVOD platforms to create new revenue streams? This article has all the answers.
