
Low-latency Video Streaming: Types And Challenges
Nobody has the patience to wait; if the content lags, users will leave and find another streaming option. This is an outcome you would want to avoid at any cost, right? Likely, there is a way to prevent this. Low latency is what you need for your streaming. With it, you no longer need to worry about lagging, buffering, and content delivery delays.
So, what is this low-latency, and how exactly does it help with buffering and delays? This article has all the answers. Read on to find out.

Key Takeaways
- Low-latency video streaming reduces the time between content capture and viewer playback, ensuring instant delivery.
- By minimizing delays, low-latency streaming boosts viewer engagement and provides a more interactive experience between the audience and content creators.
- Different low-latency video streaming protocols are available to meet the specific needs of users and service providers, allowing for customized streaming solutions.
- Offering low-latency streaming can strengthen your reputation among streaming services, attracting more viewers and potentially increasing revenue.
What is Low Latency?
Low latency is the minimal delay between a user's action and the system or network's response, typically measured in milliseconds. This concept is important in live streaming, where "live" doesn't always mean it’s live.
Traditional live streaming often has a noticeable delay (usually a minute or two) between when the content is captured and when viewers actually see it on their screens.
On the other hand, low-latency streaming delivers video content over the internet with minimal delay, bringing the viewing experience closer to real time.
How Low-latency Video Streaming Works
Traditional streaming methods often involve significant delays due to buffering, slow encoding, and network issues, sometimes taking seconds or even minutes. Low latency solves this problem by minimizing the delay between the video source, such as a content provider, and the viewer, aiming to reduce latency to just a few milliseconds or less.
Here are the primary methods and technologies behind low-latency video streaming:
Low-latency Video Streaming Protocols
Low-latency streaming often relies on specialized protocols like Low-latency HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) and others designed to minimize buffering times. These protocols enable faster data transmission, enhancing the interaction between content and viewer, particularly during live events.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Many low-latency streaming systems use adaptive bitrate streaming to adjust video quality based on the viewer’s internet speed. This ensures uninterrupted playback by automatically lowering the video quality when necessary, providing a smooth viewing experience regardless of network conditions.
Edge Computing
Using edge computing in Low-latency streaming processes data closer to the viewer using edge servers. Unlike traditional cloud processing, this approach reduces latency by minimizing the distance data needs to travel, delivering a faster and more immersive experience for users.
Chunked Data Transmission
Low-latency video streaming breaks video content into smaller chunks, transmitting small packets of data more quickly to viewers. This reduces processing time and enhances the viewing experience by speeding up the content delivery process.
Efficient Encoding
Encoders play a crucial role in low-latency video streaming protocols by compressing video content efficiently without sacrificing quality. This not only reduces delays but also allows for high-quality streaming even with limited bandwidth.
Minimal Delay Streaming
By using low-latency streaming techniques, you can deliver content with a delay as low as two to six seconds—a substantial improvement over traditional streaming. According to Forbes research, Americans pay an average of $46 per month for streaming services, making offering a high-quality, low-latency experience that meets these expectations essential.
Benefits of Low-latency Video Streaming
Low-latency video streaming offers numerous advantages that greatly enhance viewer engagement, user satisfaction, and interactivity. Here are some of the key benefits:
Viewer Engagement
Low-latency video streaming significantly boosts viewer engagement by reducing delays, making interactions feel more immediate. Real-time engagement during live events, such as sports, auctions, or Q&As, creates an immersive experience that fosters audience loyalty. This stronger connection can help boost your reputation among content creators and streaming service providers.
Improved User Experience
With Low-latency video streaming, buffering and lag can be minimized, providing viewers with a smoother, uninterrupted experience. This increase in satisfaction is important—research shows that 78% of viewers will switch to another video after the third buffering interruption, further underscoring the importance of a seamless streaming experience.
Enhanced Interactivity
Low-latency enables more interactive features like live polling, real-time commentary, and instant feedback, allowing viewers to actively participate in events. This immediate engagement makes streams more exciting, whether for voting, betting, or sharing thoughts, fostering a deeper connection between content creators and audiences.
Competitive Edge
Offering low-latency streaming can set your platform apart by providing viewers with real-time, high-quality experiences, helping you grow a loyal audience. In a market where 83% of U.S. consumers have at least one streaming subscription, low latency is a valuable differentiator that boosts credibility and attracts more users.
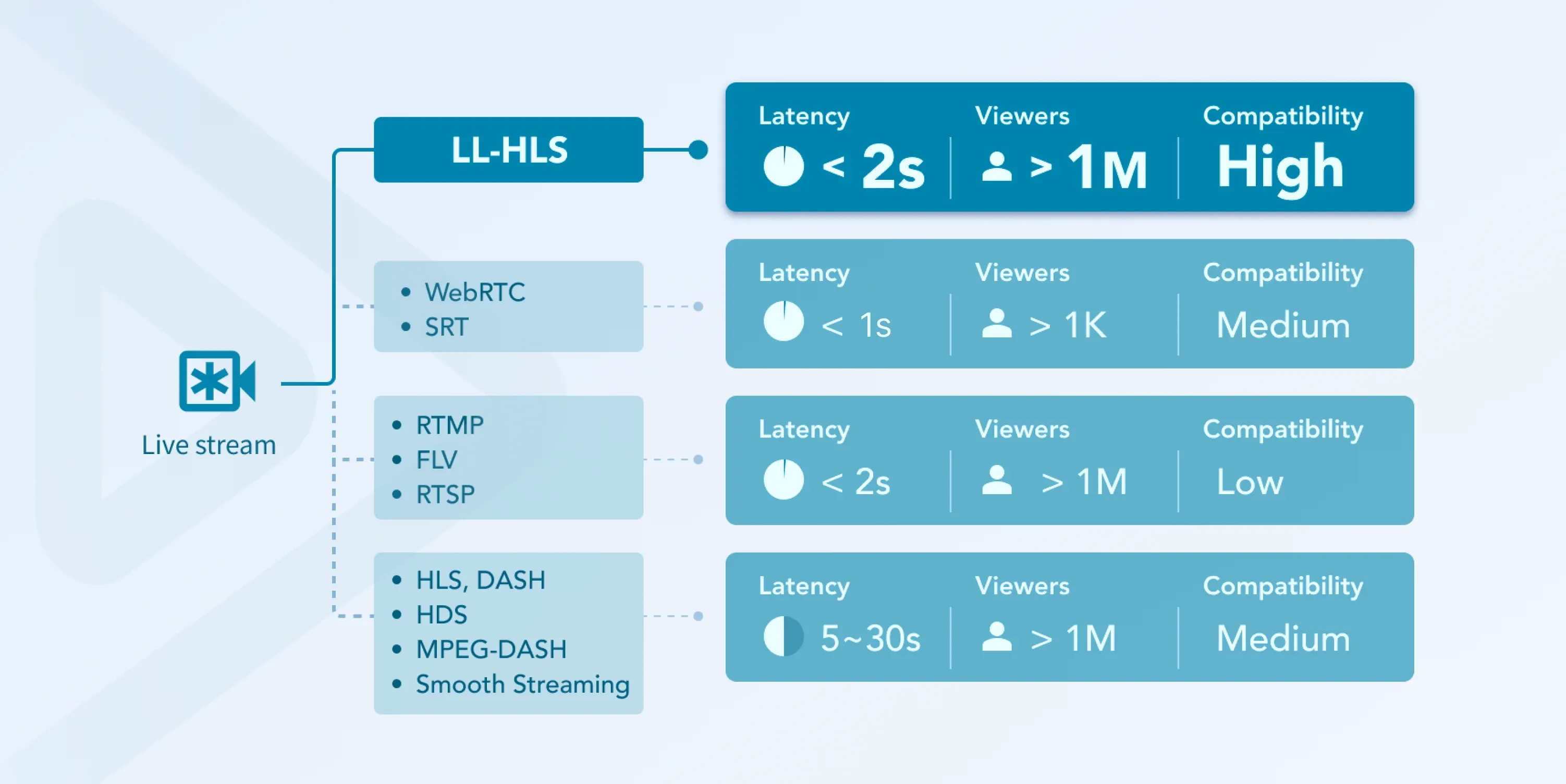
Low-latency Streaming Protocols
There are several types of Low-latency video streaming protocols, each designed to address specific content delivery needs.
 Here are some of the most widely used:
Here are some of the most widely used:
LL-HLS (Low-latency HTTP Live Streaming)
Developed by Apple, LL-HLS is an extension of the traditional HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol. It reduces delay by using smaller segment sizes and preloading hints, enabling faster content delivery. LL-HLS is widely used for applications that require quick delivery without compromising quality, making it ideal for sports and live events.
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication)
WebRTC is a powerful protocol for creating peer-to-peer connections. It enables real-time audio and video communication with minimal delay. It’s commonly used for applications like video calls, live chats, and interactive games where immediate feedback is essential.
SRT (Secure Reliable Transport)
SRT is an open-source protocol designed to deliver high-quality video across unpredictable networks. It excels in minimizing data loss and maintaining low-latency, even in challenging conditions, making it suitable for professional broadcasts and remote video production.
RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol)
Initially developed by Macromedia for Flash, RTMP remains popular for live streaming thanks to its low delay speeds. Despite declining Flash playback, RTMP is still widely used for its fast streaming capabilities, particularly on platforms with custom or legacy setups.
Low-latency DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP)
Low-latency DASH is an adaptation of the DASH protocol, using chunked transfers and smaller data segments to reduce delay. It’s suitable for scalable, high-quality streaming, making it popular for large-scale broadcasts and on-demand video services.
Each of these Low-latency video streaming types provides unique advantages, allowing content creators to choose the best option based on their specific streaming needs and audience expectations.
Types of Streaming Latency
There are three main types of latency: Standard, Low, and Ultra-low latency.
| Latency Type | Description | Latency Level | Protocols Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Latency | Traditional streaming without modification. Ideal for TV shows, pre-recorded content, and virtual events. | 6–18 seconds | HLS, DASH |
| Low Latency | Shorter delay suited for near real-time apps. Balances responsiveness with minimal buffering. Great for interactive live events. | 2–6 seconds | DASH, LL-HLS, RTMP |
| Ultra-low Latency | Delivers almost instant playback. Best for real-time interactions like auctions, gaming, or live Q&A. | 0.2–2 seconds | WebRTC, SRT |
Challenges in Achieving Low-Latency Video Streaming
While Low-latency video streaming brings numerous benefits, achieving it comes with several challenges:
Network Limitations
Slow internet speeds or unstable network connections can lead to buffering and delays, negatively impacting the viewer’s experience. Low-latency streaming requires stable, high-speed connections to ensure smooth playback.
Encoding Delays
Improper or slow encoding can add unnecessary delays to video delivery. Optimizing encoding settings is crucial to maintaining low latency, as inefficient encoding increases processing time and disrupts the real-time experience.
Protocol Limitations
Some traditional protocols don’t support Low-latency video streaming requirements, limiting streamers' options and potentially reducing the viewer’s experience. You may need to adopt newer protocols or hybrid solutions for optimal performance.
High Costs
Implementing advanced Low-latency technologies can be costly, especially for smaller organizations or content creators just starting out. Equipment, protocol licensing, and increased bandwidth requirements can quickly add up.
Scalability Issues
As viewership grows, maintaining low latency becomes more challenging. Scaling streaming services with low latency requires additional resources and infrastructure, which can strain finances, particularly for small-scale operations.
Quality Trade-Offs
Achieving low latency often requires increased compression, which can compromise video quality. Balancing latency with resolution and clarity is essential, as overly compressed streams can detract from the viewer’s immersive experience.
Syncing Issues
Network issues can create discrepancies between audio and video streams, causing them to fall out of sync. This can significantly disrupt the viewing experience, requiring careful management of network stability and synchronization settings.
These challenges highlight the need for thoughtful planning and reliable infrastructure to successfully implement low-latency video streaming and meet performance and quality standards.
Start Low-latency Streaming With inoRain
inoRain is here for your low-latency streaming needs. We use advanced techniques to minimize delays while maintaining high-quality content delivery through:
- Optimized Encoding: Our robust tools are designed to maximize encoding speeds without compromising content quality. This ensures a seamless, high-quality viewing experience, even for real-time broadcasts.
- Flexible Protocol Options: inoRain supports various Low-latency protocols designed to reduce streaming delays. By choosing the protocol that best suits your needs, you can enhance the viewing experience, creating smoother and more responsive interactions.
- Audience Insights: With inoRain’s data collection tools, you can gather valuable audience insights, which allow for more personalized content and foster a stronger connection with viewers.
- Real-Time Monitoring: inoRain’s monitoring tools enable you to track live streams and make instant adjustments, ensuring a stable stream without interruptions.
Ready to elevate your streaming game? Contact us for advanced low-latency video streaming solutions and deliver a seamless, high-quality experience that keeps your viewers coming back.
Conclusion
Low-latency video streaming transforms audience engagement by delivering real-time, immersive content across multiple platforms. It minimizes delays and enhances the viewer experience, allowing for smoother, more interactive connections between your stream and your audience.
This improved responsiveness boosts engagement and sets your platform apart in an increasingly competitive market.
FAQs
What is low latency?
Low latency describes the brief delay between a user's input and the system or network's reaction, typically measured in milliseconds.
Why do I need low latency for streaming?
Low latency is needed to reduce the delay between live events and what viewers see, ensuring real-time and smoother interaction. It avoids lagging and makes the streaming experience buffer-free and enjoyable.
Which streaming protocols support low latency?
Several different protocols are designed primarily to support low-latency, such as LL-HLS (Low-latency HLS), WebRTC, SRT (Secure Reliable Transport), RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol), and Low-latency DASH.
How can I reduce latency in my video stream?
To reduce latency in your video stream, select low-latency protocols like WebRTC, optimize encoding settings for faster processing, and use adaptive bitrate streaming to adjust quality based on network conditions. Additionally, edge computing can minimize data travel distance for quicker delivery.
What’s the difference between low-latency and ultra-low-latency video streaming?
Low-latency video streaming typically keeps delays under two seconds, ideal for live interactions. Ultra-Low-latency video streaming, however, reduces delays to under one second, which is crucial for applications needing instant feedback, like online gaming or financial trading.
Co-founder / CTO
Armen is the CTO and Co-Founder of inoRain OTT and Co-Founder of HotelSmarters, specializing in advanced streaming technologies, OTT strategy, and interactive TV systems. He builds scalable end-to-end video delivery solutions and drives technical innovation across hospitality and streaming platforms, bridging complex engineering with practical business impact.

What is OTT? Benefits and 5 Types of OTT Services
This article has all the answers to what is an OTT platform, how OTT works and the different types of OTT services

What is OTT Analytics? Key Metrics And Tools
In this article, we uncover what OTT analytics is, the top metrics and tools required to keep your OTT platform ahead of the curve - and the competition.

What is SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand)? 2026 Guide
What is SVOD, how does it work, and why are businesses turning to SVOD platforms to create new revenue streams? This article has all the answers.
