
How to Set Up a Video Streaming Server: Key Components
Whether you’re a media company or an independent content creator, understanding how a server works is key to providing seamless streams to your audience.
A well-optimized server for video streaming ensures smooth content delivery, helps you scale as your audience grows, and significantly boosts the overall user experience.
This guide will walk you through the vital components of a video-on-demand server and offer a detailed setup process tailored to your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Delivering high-quality content to large audiences depends on understanding video streaming servers, whether self-hosted or cloud-based.
- Essential components include input sources, encoding software, storage, and a delivery network, all working together for smooth video-on-demand server performance.
- Cloud-based video streaming servers offer scalability and easier management, while self-hosted options provide more control.
- Setting up a server for video streaming requires careful planning around bandwidth, storage, and the right encoding and distribution software.
- A properly configured video streaming server can help you monetize content effectively through subscriptions or ads, enabling a steady revenue stream.
What is a Video Streaming Server?
A video streaming server is a specialized server designed to store, run, and distribute real-time or on-demand video content. It ensures safe, fast delivery by managing the distribution of video files to multiple users at once. Unlike standard web servers, a server for video streaming is built to handle large amounts of video data.
A video streaming server uses protocols like the Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) and HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) to ensure smooth playback, reduce buffering, and adjust video quality based on the viewer's internet connection.
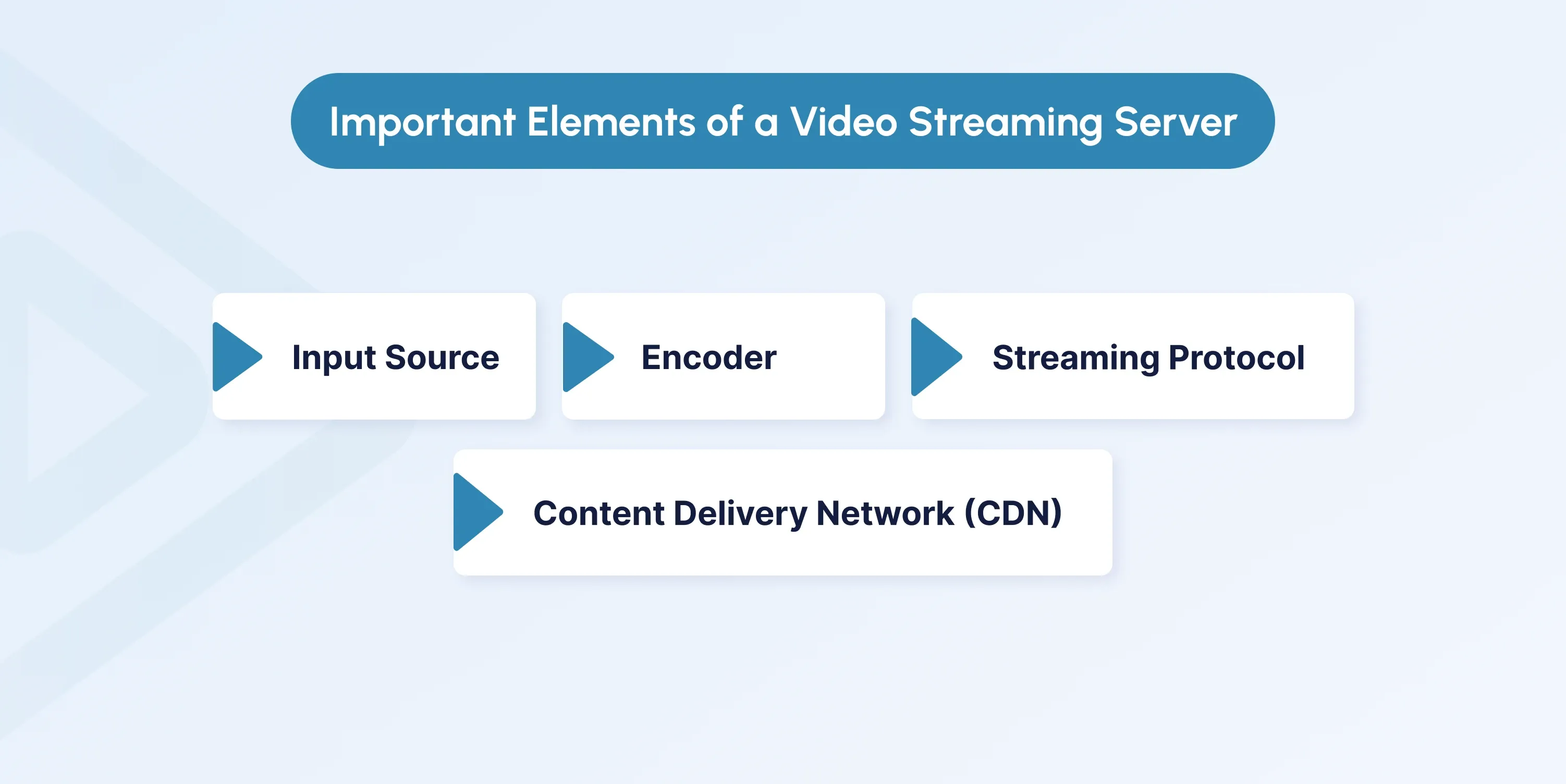
Key Components of a Video Streaming Server
A video streaming server relies on several key components to ensure smooth content delivery and a great user experience.
 Let’s break down the four fundamental parts:
Let’s break down the four fundamental parts:
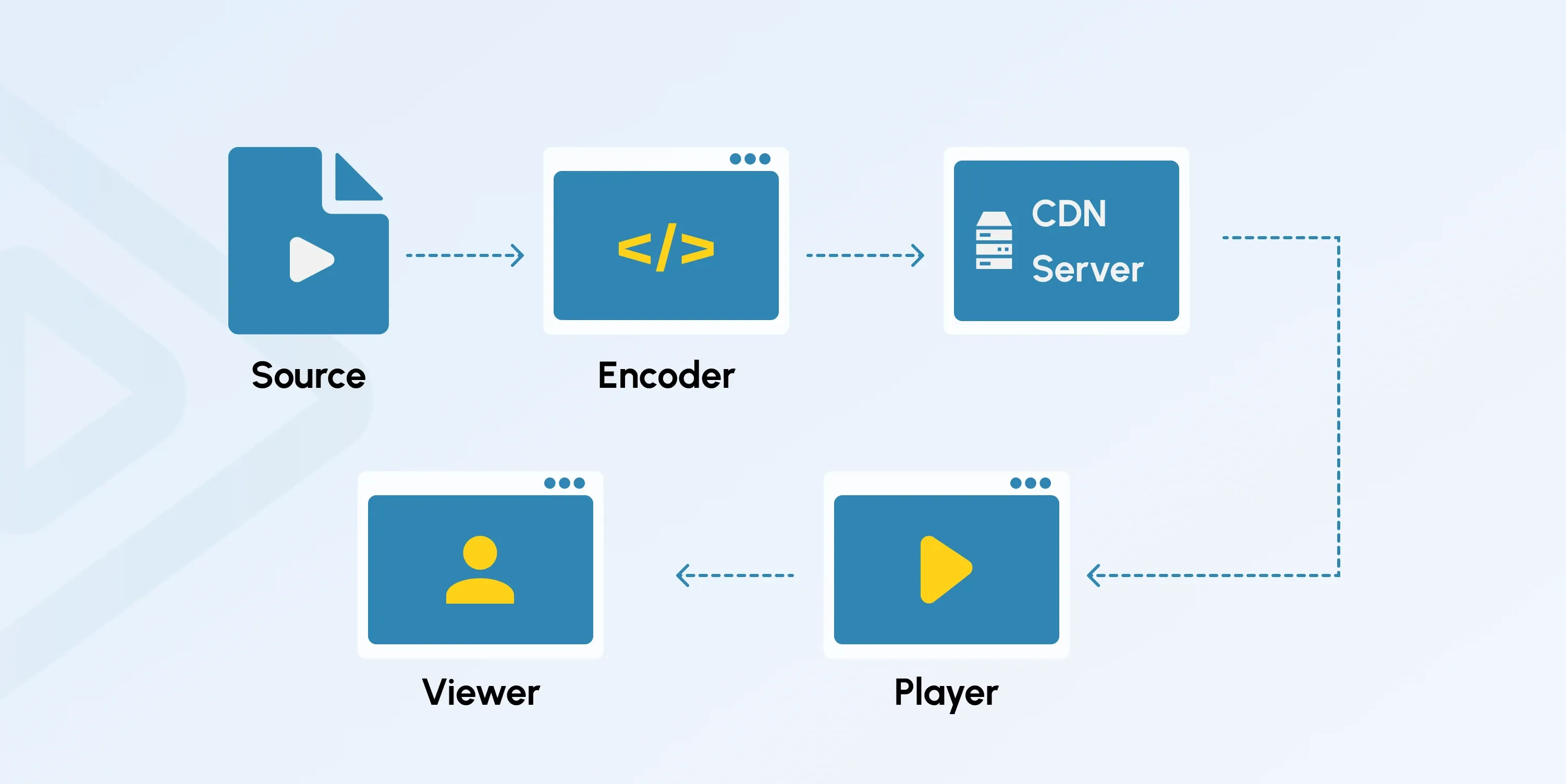
Input Source
The input source provides the raw video content to be streamed. This could be a live video feed from cameras, a pre-recorded video file, or other sources like media servers or satellite feeds. The input source sets the foundation for what your audience will eventually see. For live streaming, encoders and video capture devices convert these signals into a digital format suitable for online transmission.
Encoder
An encoder is crucial for transforming raw video data from the input source into a format optimized for streaming. Using codecs like H.264, H.265, or VP9, the encoder reduces file size to minimize buffering and allow quicker load times. For real-time streaming, the encoding process happens instantly, ensuring your viewers can enjoy live feeds without noticeable delays. Having a solid server for video streaming helps enhance this process even further.
Streaming Protocol
The streaming protocol governs how video data is transmitted from your server for streaming video to your viewer's device. As mentioned, commonly used protocols include Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) and HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). These protocols manage adaptive bitrate streaming, so viewers with slower connections still get smooth playback without constant buffering issues.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A video streaming server works with a content delivery network (CDN) to distribute video content more efficiently. CDNs are networks of servers spread across different geographic locations that work together to deliver your content faster. A CDN helps reduce latency and improve video quality by storing video files near your viewers. CDNs also ensure scalability, so your video-on-demand server can handle thousands, or even millions, of simultaneous viewers without hiccups.
Self-Hosted vs. Cloud-Based Streaming Servers
When learning how to set up a video streaming server, one of the biggest decisions is whether to use a self-hosted or cloud-based solution. Each option has pros and cons, and the best choice depends on your specific needs, available resources, and long-term goals.
Self-Hosted Streaming Servers
If customization is a priority, a self-hosted video streaming server gives you complete control over your setup. With this option, you own the hardware, software, and network, allowing you to tailor everything to your exact streaming needs, whether it's implementing custom security features, adjusting video quality, or enhancing server performance.
However, the initial setup costs can be significant. Investing in physical hardware, high-speed internet, networking equipment, and ongoing maintenance can quickly become expensive.
A basic self-hosted system can cost anywhere from $3,000 to $10,000, depending on your needs. Scaling a self-hosted solution often means buying more hardware, which is both costly and time-consuming.
This setup requires a skilled IT team to handle server upgrades, performance monitoring, and troubleshooting. All this expertise adds to the overall video streaming server cost, which can increase substantially over time.
Cloud-Based Streaming Servers
Cloud-based video streaming servers offer ease of use and greater scalability. Major providers like Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS deliver cloud solutions that provide quick and straightforward setup processes, making them ideal for businesses with limited IT resources.
One of the biggest advantages of cloud-based streaming servers is their scalability. These servers can adjust resources based on real-time demand, ensuring that your video-on-demand streaming server can handle the load no matter how many viewers are tuning in.
Gartner reports that by 2025, 80% of businesses will migrate to cloud-based platforms for higher flexibility and ease of use.
While these solutions often have no upfront hardware costs, the pay-as-you-go pricing model can result in higher long-term expenses. For businesses with high bandwidth needs, cloud services might seem cheaper at first, but can lead to substantial bills over time.
A cloud-based video streaming server is great for flexibility, but remember that continuous usage and growing audiences can drive up costs.
Choosing the Right Streaming Server
Your specific requirements will be crucial when deciding between a self-hosted and a cloud-based video streaming server.
If You…
- Seek full control and customization
- Want to invest in the required technical expertise and infrastructure
- Aim for reduced long-term costs with tailored infrastructure.
Choose a self-hosted streaming server
If You…
- Want low startup expenses
- Plan rapid scalability and user-friendly operations
- Lack the technical resources to maintain physical infrastructure
Choose a cloud-based streaming server
If you still struggle to make a choice. Here are some more tips. Assess your organization’s budget, technical capacity, and growth expectations. Explore both options—self-hosted and cloud-based—to help you determine the most effective streaming setup.
Whether you’re considering the best video streaming server or evaluating video streaming server hosting options, understanding your needs will guide you toward the right choice.
How to Set Up a Video Streaming Server
Setting up a video streaming server requires careful planning and the right mix of hardware, software, and configuration to ensure seamless streaming.
 Whether you choose a self-hosted video streaming server or a cloud-based solution, following these steps will help you get started.
Whether you choose a self-hosted video streaming server or a cloud-based solution, following these steps will help you get started.
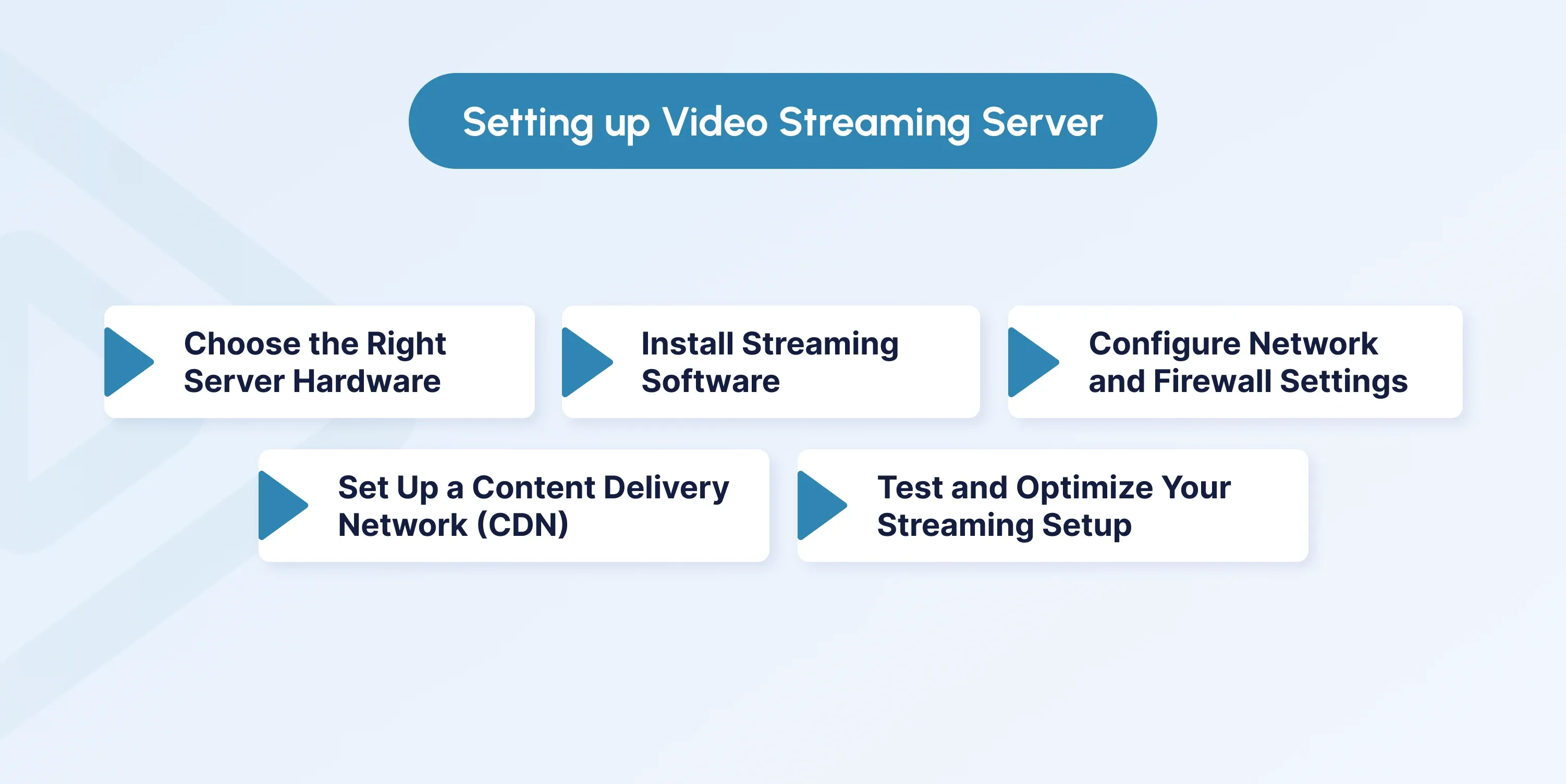
Step 1: Choose the Right Server Hardware
The first step in setting up a server for video streaming is selecting suitable hardware. You'll need a robust server with a fast processor, plenty of RAM, and a stable internet connection. Sufficient storage space is also crucial for managing your video files and streams. For small-scale streaming, a high-performance PC might be sufficient, but large-scale setups require dedicated hardware or a data center environment.
For cloud-based video streaming servers, there’s no need to worry about physical hardware. Instead, focus on selecting the right cloud provider and plan, such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, all of which offer flexible server configurations. AWS alone holds 33% of the global cloud infrastructure market, making it a popular choice for businesses worldwide.
Step 2: Install Streaming Software
Once your hardware or video streaming server is ready, the next step is to install streaming software. The software you choose determines how your video streams are encoded, managed, and delivered. Popular options include:
- FFmpeg: A command-line tool used by advanced users for media encoding and streaming.
- Wowza Streaming Engine: A comprehensive live and on-demand streaming solution with many customization options.
- OBS Studio: Free and open-source, widely used for smaller-scale live streaming.
Set your software’s bitrate, resolution, and video format to match your requirements. Adjust these settings to ensure optimal performance on various devices.
Step 3: Configure Network and Firewall Settings
Network configuration is essential when setting up a video streaming server. Whether you're using a server for streaming video from home or a dedicated service, ensuring high-bandwidth internet access is crucial.
You must open the necessary ports and configure your firewall so video streams pass through seamlessly. This guarantees your server can deliver smooth, high-quality streams to users.
If you're managing the setup yourself, prioritize traffic on your server for video streaming within your router settings. This ensures your video data transmission isn't competing with other network tasks, improving overall stream quality.
While cloud-based video streaming server hosting often handles this automatically, it’s still vital to make sure your network can support consistent, high-quality streams, especially for demanding tasks like video-on-demand streaming.
Step 4: Set Up a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN can make a world of difference in optimizing global streaming. A CDN distributes your video content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing latency and improving user load times. This is particularly useful for catering to an international audience or managing a video-on-demand server. The faster the data reaches your viewers, the better the streaming experience.
CDN providers like Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, and Akamai are top choices for improving performance. They help ensure fast and reliable delivery by reducing the physical distance between your viewers and your server for video streaming.
Whether you're hosting a video-on-demand streaming server or live streaming events, integrating a CDN improves reliability and speeds up access across the globe.
Step 5: Test and Optimize Your Streaming Setup
Before going live, it’s vital to test your entire setup. Ensure the video streaming server can handle expected traffic volumes and that the audio and video quality meet your standards. Perform stress tests to ensure your network and hardware can scale up to meet high demand. Platforms like OBS Studio or Wowza are great for testing different streaming setups.
Regularly monitoring the server’s performance using tools that check stream quality, server load, and bandwidth consumption is also a good idea. This will allow you to fine-tune encoding settings and make adjustments as needed. Constant optimization delivers flawless video across various devices and network conditions.
inoRain for Video Streaming Needs
inoRain provides scalable and adaptable video streaming server solutions tailored for businesses and content creators alike. Whether you’re seeking a cloud-based server for video streaming or a self-hosted option, we offer a reliable platform that meets your diverse needs.
Our high-performance servers are designed to support a global audience, ensuring flawless streaming through dependable network architecture and seamless integration with leading content delivery networks.
Whether you’re interested in learning how to set up a video streaming server quickly and efficiently or looking for a video-on-demand streaming server, inoRain can help you succeed. Contact us to learn more.
Conclusion
Building a smooth streaming system starts with understanding the key components of a video streaming server, choosing between self-hosted or cloud-based options, and ensuring your infrastructure is prepared.
A properly configured server for video streaming boosts platform performance, offers scalability, and opens up income opportunities for businesses and creators.
FAQs
What are the key differences between self-hosted and cloud-based streaming servers?
Cloud-based video streaming servers are perfect for businesses looking for scalability, easier management, and lower upfront costs.
On the other hand, self-hosted servers for streaming video provide complete control over your infrastructure, but they require more maintenance and technical know-how. It really comes down to your specific needs and resources.
How much bandwidth do I need for a video streaming server?
The amount of bandwidth you need for your video streaming server depends on several factors, including bitrates, video quality, and the number of viewers.
For instance, if you aim for HD streaming, you'll require higher bandwidth to ensure flawless, uninterrupted streaming. It’s all about delivering the best experience for your audience.
Can I monetize content on my video streaming server?
Absolutely! You can monetize your content on a video streaming server through various methods, such as subscriptions, advertisements, or pay-per-view models. The specific options available will depend on your server type and how you've set up your platform, but there are plenty of ways to generate revenue from your content.
Co-founder / CTO
Armen is the CTO and Co-Founder of inoRain OTT and Co-Founder of HotelSmarters, specializing in advanced streaming technologies, OTT strategy, and interactive TV systems. He builds scalable end-to-end video delivery solutions and drives technical innovation across hospitality and streaming platforms, bridging complex engineering with practical business impact.

What is OTT? Benefits and 5 Types of OTT Services
This article has all the answers to what is an OTT platform, how OTT works and the different types of OTT services

What is OTT Analytics? Key Metrics And Tools
In this article, we uncover what OTT analytics is, the top metrics and tools required to keep your OTT platform ahead of the curve - and the competition.

What is SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand)? 2026 Guide
What is SVOD, how does it work, and why are businesses turning to SVOD platforms to create new revenue streams? This article has all the answers.
