FAST Channel
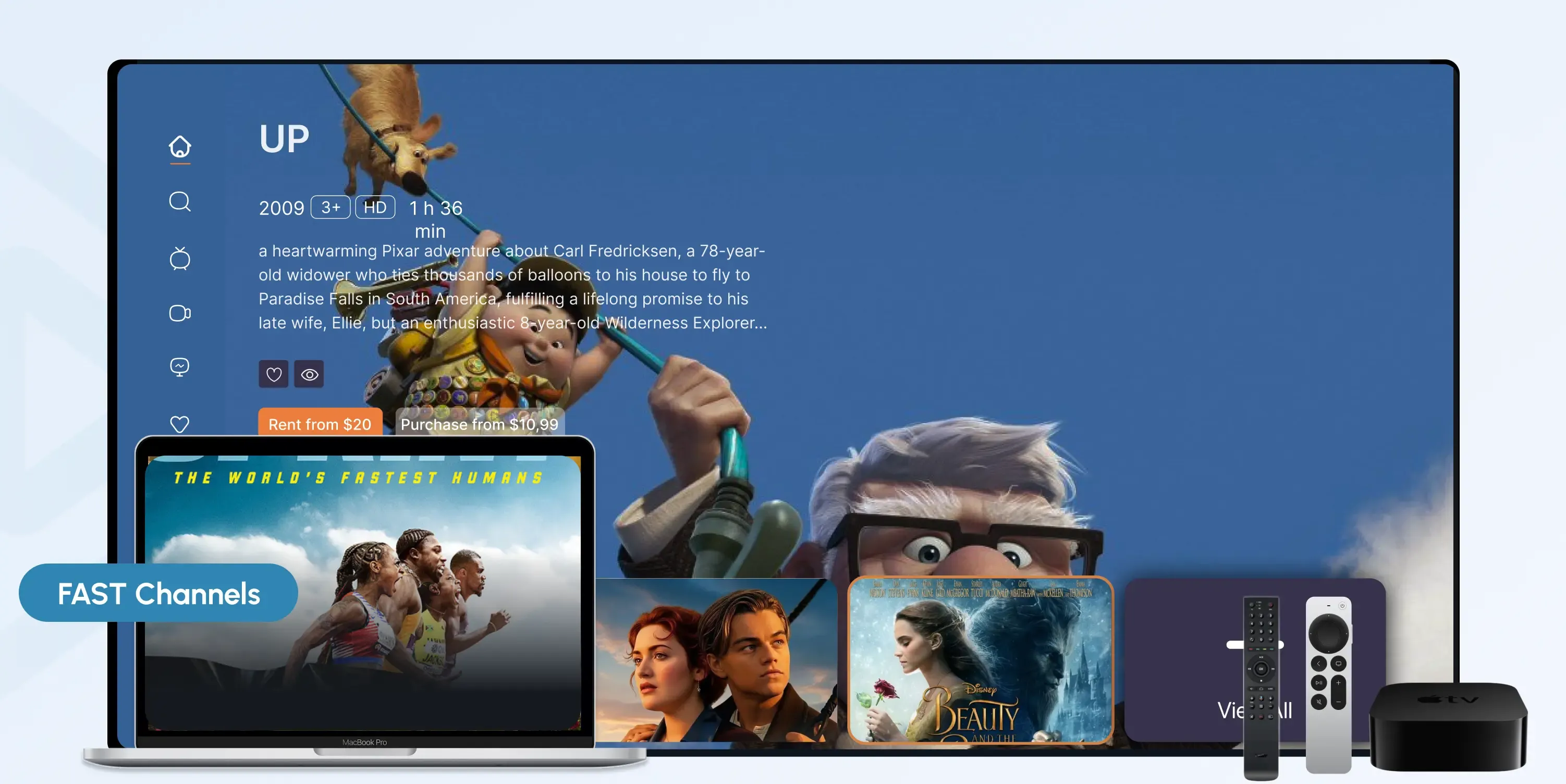
What Is a FAST Channel?
FAST Channels (Free Ad-Supported Streaming Television channels) are live, linear-style streaming TV channels. Viewers can watch FAST Channels for free with ads, and providers monetize content through those advertisements.
Think of FAST Channels as the modern digital equivalent of traditional broadcast or cable TV, but delivered over the internet. It's streamed through smart TVs, OTT platforms, or streaming apps.
Note: FAST is not the same as AVOD(Ad-Supported Video on Demand). Both allow content access for free with ads, but…
FAST delivers scheduled, linear channels for passive viewing, similar to traditional TV, but over the internet.
AVOD lets users choose and watch specific videos on demand, with ads inserted before, during, or after playback.
Key Features of FAST Channels
Overview
- Free access: No subscription or rental fee; users only need to watch ads.
- Ad-supported: Monetization comes from mid-roll, pre-roll, or banner ads.
- Linear schedule: Content is played in a scheduled sequence (similar to traditional TV).
- Digital-first: Distributed over the internet, not through cable or satellite.
- Genre-specific: Often built around niche topics (e.g., crime TV, cooking, classic movies).
OTT Platforms That Offer FAST Channels
- Pluto TV
- Samsung TV Plus
- Roku Channel
- Tubi
- Xumo
How Does FAST Work? 5 Simple Steps
Step 1: Content owners (e.g., studios, media libraries) provide existing video content.
Step 2: This content is packaged into a 24/7 linear schedule with EPG.
Step 3: The stream is delivered over the internet via OTT platforms (smart TVs, apps).
Step 4: Viewers watch for free, and ads are inserted into the stream at designated breaks.
Step 5: Revenue is generated primarily through advertising, rather than subscriptions.
How FAST Channels Are Delivered
Technical Breakdown
Stage 1. Content Preparation
- Video files are transcoded into HLS or MPEG-DASH formats.
- Metadata, closed captions, and ad markers are added.
- Content is uploaded to a Video CMS or Playout System.
2. Channel Playout
- A cloud playout engine (e.g., Amagi, Wurl, Frequency) schedules content to simulate live TV.
- The output is a continuous live stream (like a playlist with transitions).
- EPG (Electronic Program Guide) is generated and sent to platforms.
3. Ad Insertion
- SSAI (Server-Side Ad Insertion) seamlessly stitches ads into the stream.
- Alternatively, CSAI (Client-Side Ad Insertion) enables the player to dynamically call ads.
- Ad Decision Server (ADS) delivers personalized or programmatic ads in real time.
4. Streaming Delivery
- The final HLS/MPEG-DASH stream is delivered via CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) for low-latency delivery across various devices.
5. Distribution
- The channel is submitted to FAST platforms, including Pluto TV, Samsung TV Plus, and Roku Channel, among others.
- These platforms handle discovery, app interface, and user experience.
6. Monetization and Analytics
- Ad impressions are tracked via SSAI logs or client-side beacons.
- Viewership data, watch time, and geo-stats are collected for optimization and reporting.
Required Tech Stack for FAST Channels
To deliver a FAST channel, several technical components are required.
Starting from a CMS (Content Management System) or playout system, video streams are scheduled and managed. Then, encoding and packaging tools convert the video files into streaming formats such as HLS or MPEG-DASH.
Next stage is ad delivery when platforms use ad tech solutions. Ads are inserted using server-side ad insertion (SSAI) or client-side ad insertion (CSAI) technologies.
The content is then distributed globally using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to ensure smooth and fast streaming.
Next up, analytics tools are integrated to track performance, engagement, and revenue metrics. After collecting all the necessary information, it's time to generate an Electronic Program Guide (EPG). This is generated using tools like Gracenote or XMLTV to provide a TV-like schedule view for users.
This entire technical stack ensures the FAST channel runs smoothly, is monetized effectively, and delivers a consistent viewing experience across devices.
Overview
| Component | Purpose | Example Providers |
|---|---|---|
| CMS/Playout | Schedule and manage streams | Amagi, Wurl, Frequency |
| Encoding and Packaging | Convert to HLS/DASH | AWS MediaConvert, FFmpeg |
| Ad Tech | Insert and manage ads | Google Ad Manager, SpringServe |
| SSAI/CSAI | Deliver ads | Yospace, AWS MediaTailor |
| CDN | Deliver content globally | Akamai, Fastly, Cloudflare |
| Analytics | Track performance | Conviva, Mux, Google Analytics |
| EPG Generator | Create TV-like guides | Gracenote, XMLTV tools |
FAST Channels vs SVOD vs AVOD vs TVOD
Overview
FAST (Free Ad-Supported Streaming TV): Streams scheduled, live-style channels for free with ads, like traditional TV, but online.
SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand): Offers unlimited, on-demand content access for a recurring fee, usually ad-free (e.g., Netflix).
AVOD (Ad-Supported Video on Demand): Offers free, on-demand content with ads, allowing users to choose what to watch (e.g., Tubi).
TVOD (Transactional Video on Demand): Requires users to pay per title (either to rent or buy) with no subscription (e.g., iTunes, Amazon Rentals).
Comparison Table: FAST vs SVOD vs AVOD vs TVOD
| Model | Content Access | Type | Best For | Monetization | Target Audience | Viewer Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAST | Free | Linear (Scheduled) | Passive viewing, live-like experience | Ads (SSAI/CSAI) | Cord-cutters, casual viewers | Low (no on-demand control) |
| SVOD | Paid (subscription) | On-demand | Binge-watchers, loyal fans | Recurring subscription | Households, regular streamers | High (full control) |
| AVOD | Free | On-demand | Budget-conscious viewers | Ads | Younger users, mass audience | High |
| TVOD | Pay-per-title | On-demand | One-time viewers, new releases | One-time purchases/rentals | Niche content lovers, movie fans | High |
Why Should You Choose FAST Channels?
User Perspective:
FAST channels offer a familiar, lean-back TV experience without the cost or complexity of subscriptions. So, viewers instantly access curated content streams on smart TVs and devices, with no sign-ups or fees.
FAST is ideal for casual browsing, background entertainment, or discovering niche programming, all supported by non-intrusive ads instead of paywalls
Business Perspective:
FAST channels offer a low-cost, scalable method for monetizing video content through advertising. This means, streaming businesses can repurpose existing libraries. With this method, one can reach broad audiences via built-in smart TV distribution and earn consistent ad revenue without relying on paid subscribers
In conclusion, FAST is a win-win for both users and content providers. No one has to pay, but everyone gets what they want.
Frequently Asked Questions
Content Writer
Anush Sargsyan is a content writer specializing in B2B content about OTT streaming technologies and digital media innovation. She creates informative, engaging content on video delivery, OTT monetization, and modern media technologies. The goal is to help readers easily understand complex ideas. Her writing is the bridge between technical detail and practical insight, making advanced concepts accessible for both industry professionals and general audiences.
Related terms
AVOD (Advertising-Based Video on Demand)
Explore how AVOD works, its monetization model, and why it's popular for free streaming platforms. Read the full definition on inorain.com glossary.
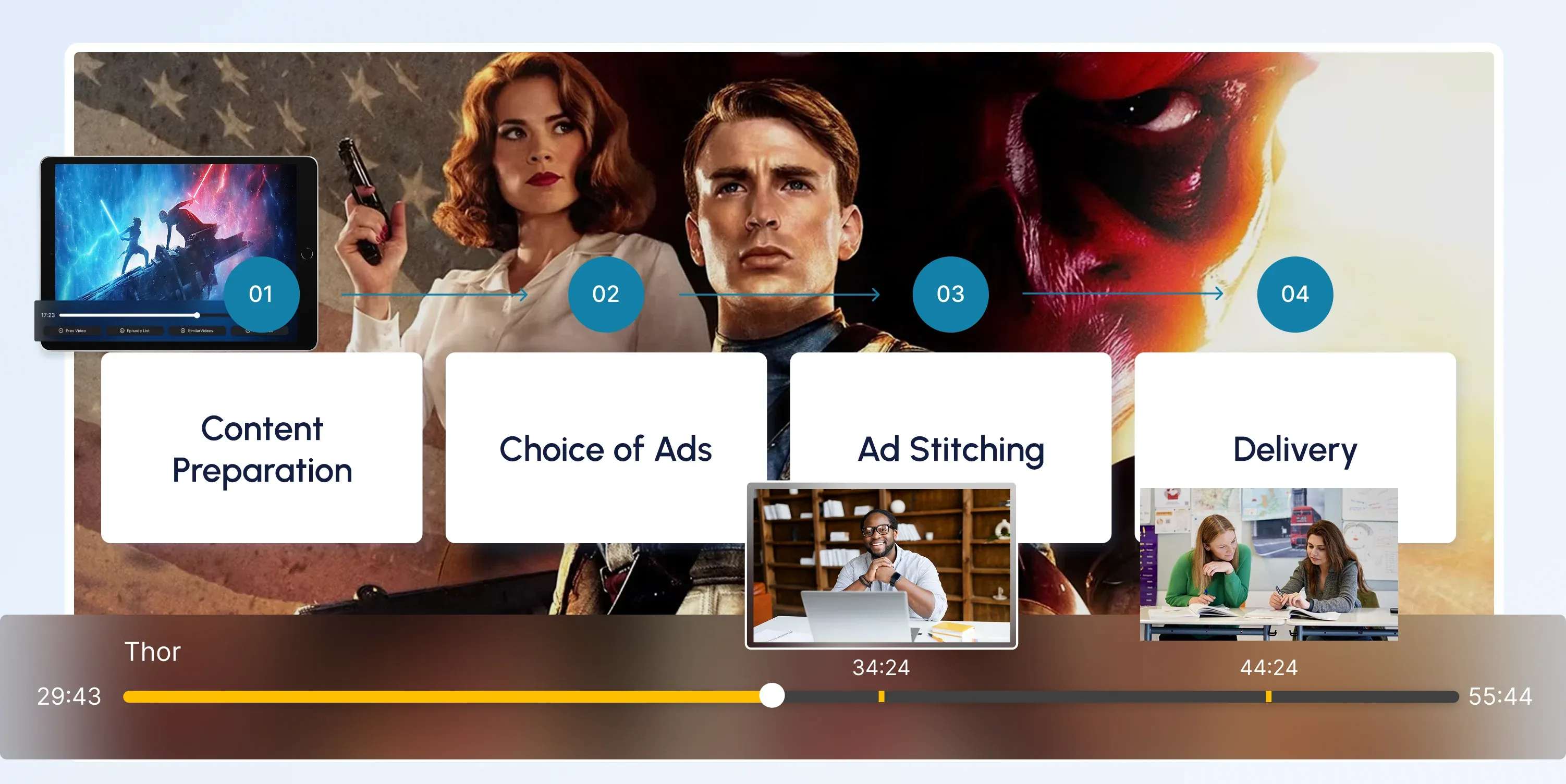
CSAI (Client-Side Ad Insertion)
Learn how CSAI delivers ads through the video player, enabling targeting, tracking, and monetization.
