AVOD (Advertising-Based Video on Demand)
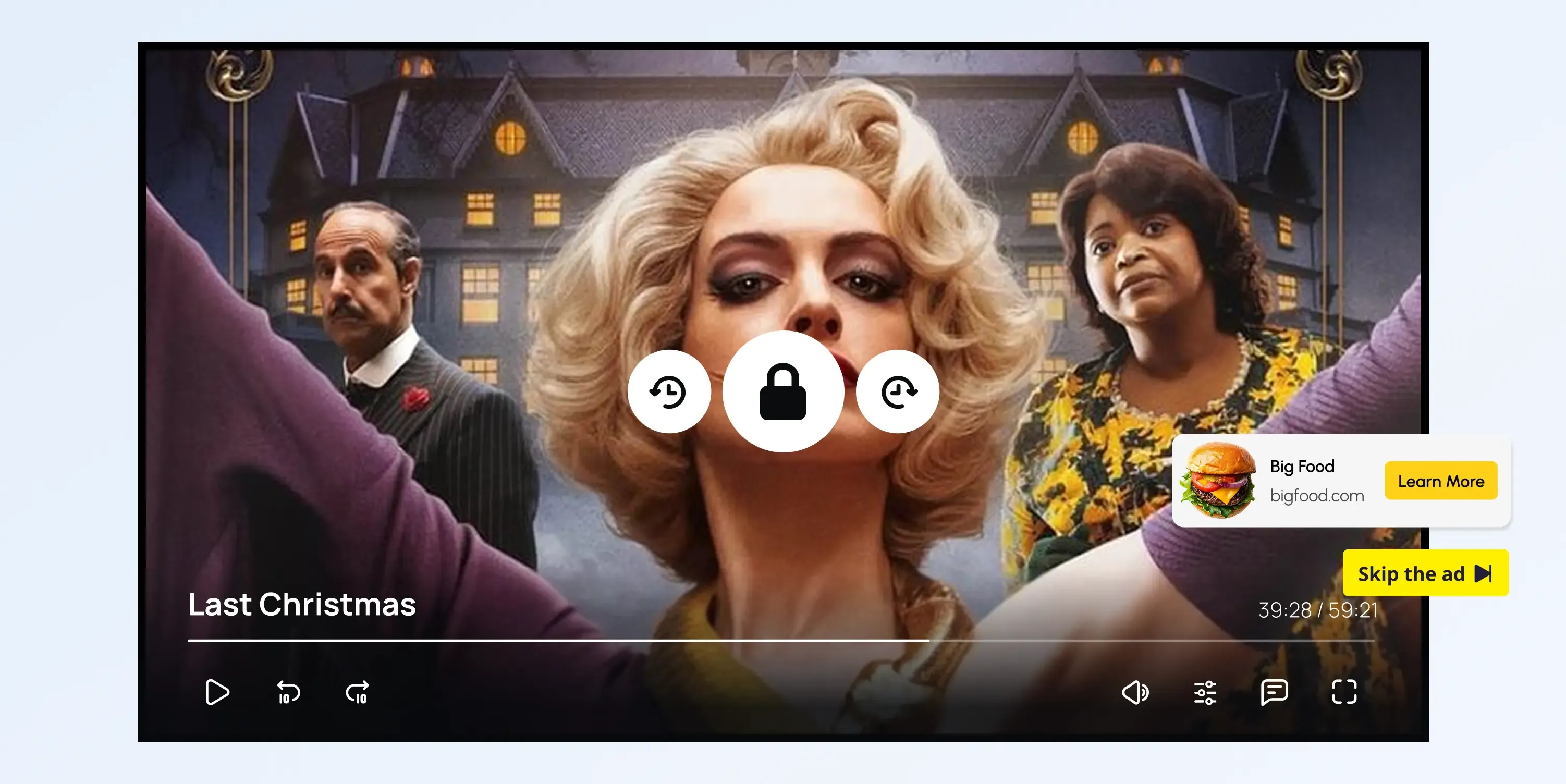
What Is AVOD?
AVOD is a streaming model where users can watch content for free, but they must view advertisements before, during, or after the video. Platforms earn revenue through ads instead of subscriptions.
What are AVOD Characteristics?
- Free Access: Users can watch content without paying a subscription fee.
- Ad-Supported: Revenue is generated through advertisements shown during playback (pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll, or display ads).
- Broad Audience Reach: Easier access attracts a wider audience, including price-sensitive viewers.
- Content Variety: Often includes movies, shows, clips, and user-generated content, depending on the platform.
- Lower Barrier to Entry: No payment is required, making it easier for new users to try the platform.
- Data-Driven Advertising: Ads are often targeted based on user behavior, location, or interests.
What are AVOD Ad Formats?
1. Pre-Roll Ads: Short video ads that play before the main content begins. _Common length: 6–15 seconds or 30 seconds.
2. Mid-Roll Ads: Ads inserted in the middle of longer content, similar to commercial breaks on TV. _Used in movies, TV episodes, or long-form videos.
3. Post-Roll Ads: Ads that appear after the content ends—less intrusive, but also less engaging for advertisers.
4. Overlay Ads: Semi-transparent banners or pop-ups overlaid on the video, often clickable, without interrupting playback.
5. Display Ads (Companion Banners): Static or animated ads shown beside or below the video player (on desktop or mobile), often used alongside video ads.
6. Interactive Ads: Engaging formats that let viewers click, choose outcomes, or explore products, enhancing ad recall and brand interaction.
7. Pause Ads: Ads that appear only when a viewer pauses the video—non-intrusive and often static or animated visuals.
8. Sponsored Content/Branded Segments: Brands sponsor a piece of content or integrate messaging directly into the video, making it part of the viewing experience.
AVOD in the VOD
The Video on Demand (VOD) ecosystem allows viewers to access video content anytime, without being tied to scheduled broadcasts.
This ecosystem is commonly structured into three main monetization models:
AVOD (Advertising-Based Video on Demand): Viewers can stream content for free, but it includes advertisements that play before, during, or after the video.
SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand): Audiences pay a recurring subscription fee to access a platform’s complete content library.
TVOD (Transactional Video on Demand): Users rent or purchase individual content titles on a pay-per-view basis.
AVOD vs SVOD vs TVOD: Main
From the User’s Perspective
| Aspect | SVOD | AVOD | TVOD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access | Unlimited (with subscription) | Free (with ads) | Pay-per-view |
| Ads | Usually ad-free | Yes, ad-supported | No ads |
| Payment Model | Monthly/Yearly | Free to watch | One-time fee per title |
| Content | Full library | Select content | Individual titles |
| User Control | High | Medium (ads interrupt playback) | High |
From the Content Provider’s Perspective
| Aspect | SVOD | AVOD | TVOD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Model | Predictable recurring income | Revenue based on ad views and impressions | Earnings per transaction (rent or buy) |
| Monetization Speed | Slower but consistent | Quick to scale with larger audiences | Instant, depending on user purchases |
| Audience Reach | Limited to paying subscribers | Widest reach due to free access | Smaller reach—only those who pay per title |
| Content Strategy | Focused on retention and exclusivity | Prioritizes high-volume, ad-friendly content | Emphasizes new, high-demand, or premium content |
| User Data Access | In-depth subscriber insights | Solid targeting data, though less detailed | Mostly purchase behavior data |
| Churn Risk | High—users can cancel anytime | Very low—no recurring commitment required | Not applicable—pay-as-you-go |
| Marketing Focus | Subscriber retention and engagement | Expanding audience and maximizing ad inventory | Title-level marketing and promotions |
5 Key Impacts of AVOD on Entertainment and Advertising
1. Expanded Audience Reach
AVOD platforms make content freely accessible, attracting broader and more diverse audiences, especially in price-sensitive and global markets.
2. Shift from Subscription to Ad-Based Revenue
Content creators and distributors increasingly rely on advertising income, especially for monetizing older, long-tail, or lower-budget content.
3. Growth of Targeted, Data-Driven Advertising
AVOD enables advertisers to deliver highly personalized and measurable ads using viewer data, outperforming traditional broadcast targeting.
4. New Life for Legacy Content
Older films and series find renewed value on AVOD platforms, generating passive revenue through ad views without extra production costs.
5. Ad Spend Reallocation and Programmatic Growth
Marketers are shifting budgets from linear TV to AVOD, using programmatic tools to reach streaming-first, ad-tolerant viewers efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Content Writer
Anush Sargsyan is a content writer specializing in B2B content about OTT streaming technologies and digital media innovation. She creates informative, engaging content on video delivery, OTT monetization, and modern media technologies. The goal is to help readers easily understand complex ideas. Her writing is the bridge between technical detail and practical insight, making advanced concepts accessible for both industry professionals and general audiences.
Related terms
AVOD (Advertising-Based Video on Demand)
Explore how AVOD works, its monetization model, and why it's popular for free streaming platforms. Read the full definition on inorain.com glossary.
CSAI (Client-Side Ad Insertion)
Learn how CSAI delivers ads through the video player, enabling targeting, tracking, and monetization.
