HVOD (Hybrid Video on Demand)
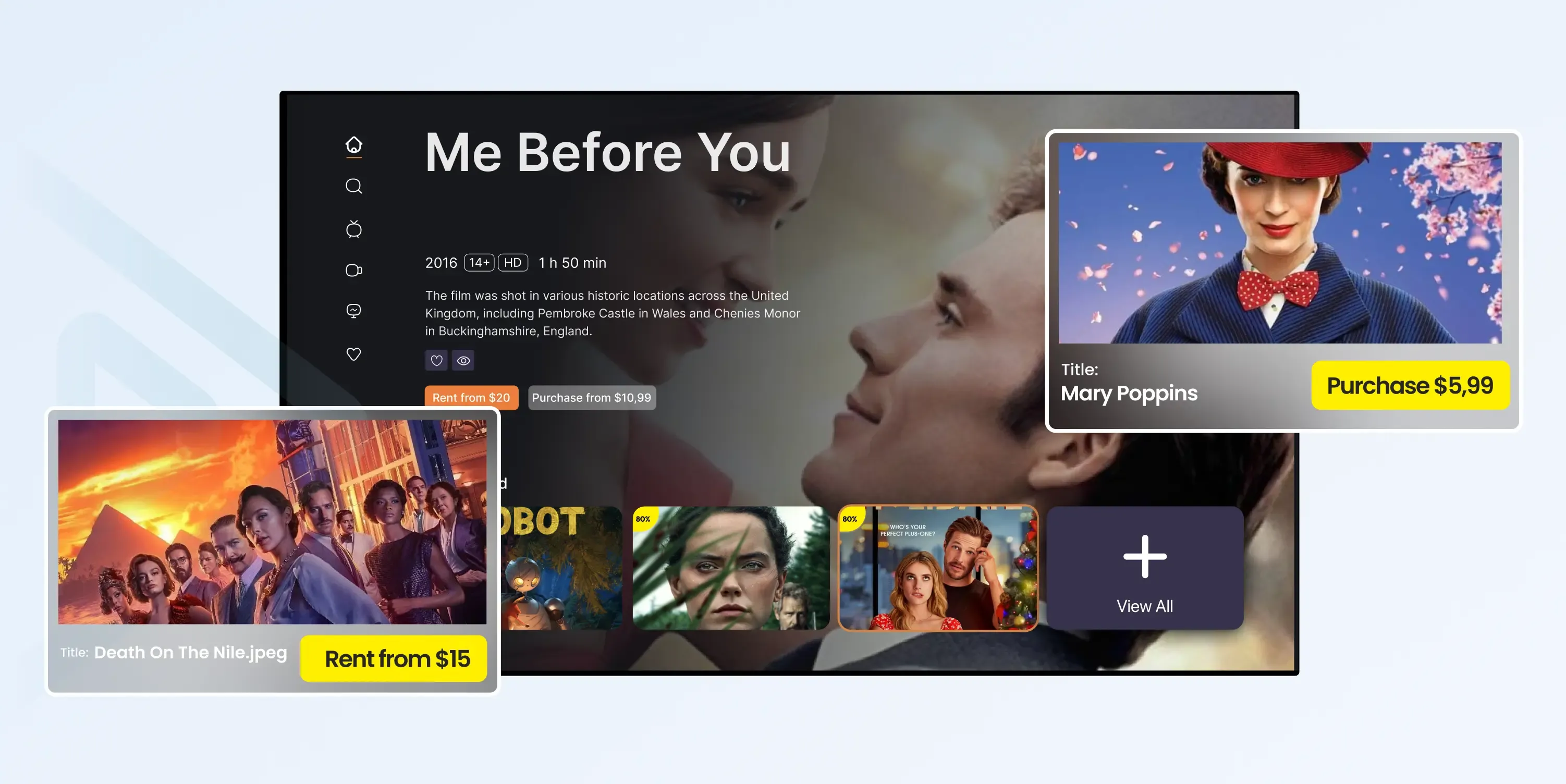
What Is HVOD?
HVOD is a video streaming model that combines multiple monetization methods like subscriptions, ads, and pay-per-view. It offers flexibility for users and maximizes revenue for content providers.
Key Features of HVOD
- Multiple Monetization Models: Combines SVOD, AVOD, and TVOD for flexible revenue streams.
- Tiered Access: Supports different content tiers based on user preferences or payment plans.
- Broader Audience Reach: Attracts both users who prefer free access and paying subscribers.
- Content Flexibility: Offers diverse content, including premium shows and free-to-access clips.
- Optimized Revenue: Balances ad revenue, subscription income, and pay-per-view earnings.
- Scalable Model: Suitable for both small platforms and large streaming services.
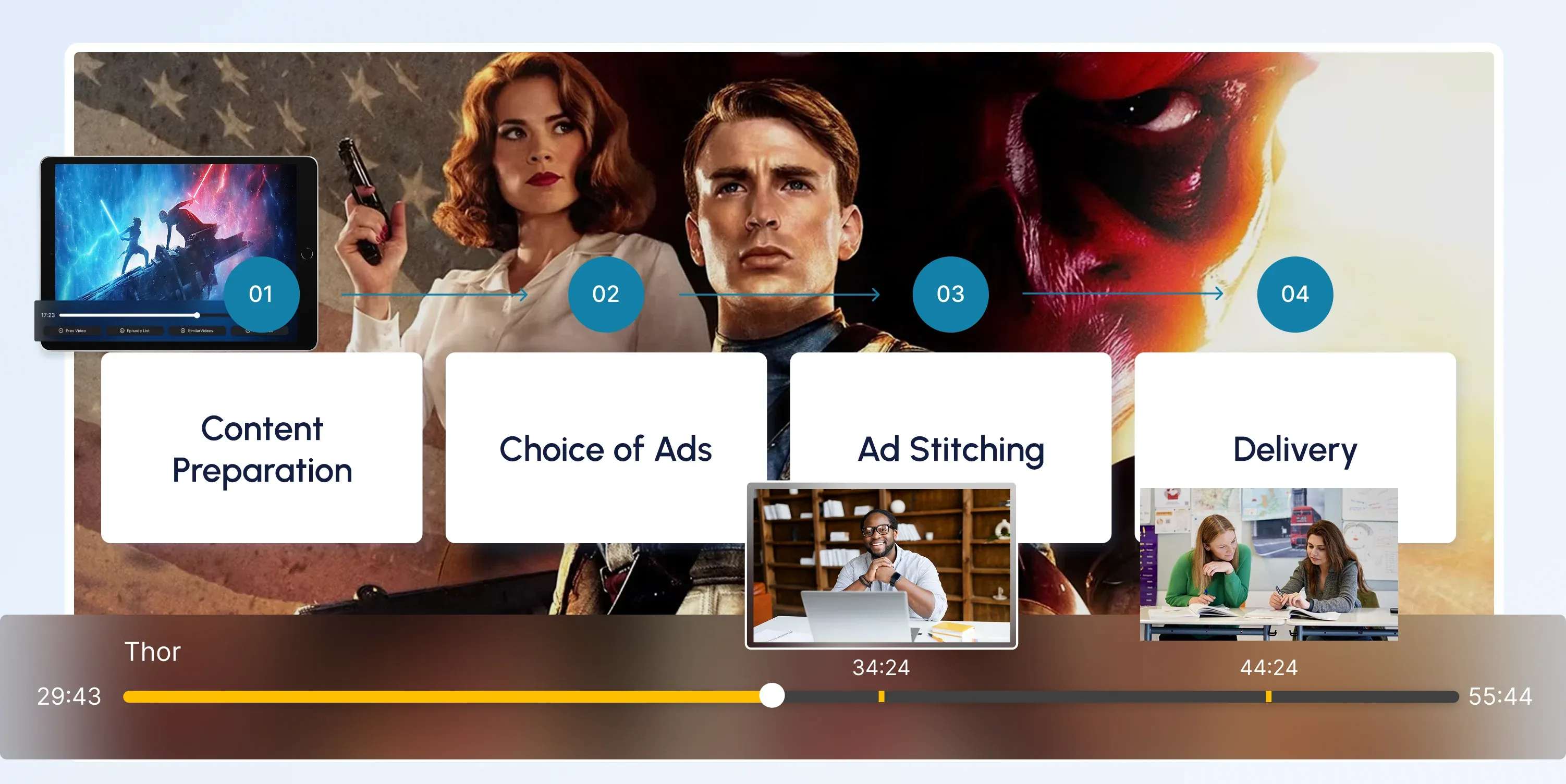
How Does HVOD Work?
Stage 1: Content Offering
The OTT platform provides a mix of free, subscription-based, and pay-per-view videos.
Stage 2: User Choice
Viewers choose how they want to access the content: free with ads, through a paid subscription, or by renting/buying content.
Stage 3: Access & Playback
Based on the user’s choice, the platform grants access and plays the content with or without ads.
Stage 4: Monetization
The service generates revenue through advertisements, subscription fees, or one-time payments.
Stage 5: User Experience
The platform may personalize content and recommendations based on viewing habits.
Technologies Behind HVOD
1. User Segmentation
The process of classifying users into distinct groups based on subscription status, viewing behavior, location, device type, or payment history.
Goal: Deliver personalized content, pricing, and ad experiences to each segment.
Examples:
Users with free access → see AVOD content with ads
Paid subscribers → access SVOD library without ads
Occasional users → prompted with TVOD offers for new releases
2. Content Access Control
A rules-based system that restricts or grants access to specific videos based on user entitlements.
Goal: Ensure only authorized users can view specific content based on their access level (free, subscriber, or one-time purchaser).
Examples:
SVOD content: only visible to logged-in subscribers
TVOD content: unlocked after payment
AVOD content: available to all, but with ads
3. Payment Processing
A secure and flexible payment infrastructure that supports subscriptions, one-time purchases, and upgrades.
Goal: Enable fast, reliable financial transactions with support for multiple payment methods and currencies.
Examples:
Monthly billing via Stripe or PayPal for SVOD
Credit card or mobile payments for TVOD purchases
Support for auto-renewals, trials, and refunds
4. Ad Insertion
The use of Dynamic Ad Insertion (DAI) or Server-Side Ad Insertion (SSAI) to deliver personalized ads during AVOD playback.
Goal: Monetize free users through targeted, non-disruptive ad experiences.
Examples:
Pre-roll, mid-roll, and post-roll ads
Personalized ads based on user profile and device
Real-time ad stitching into video streams
5 HVOD Platforms
1. Hulu
This OTT platform offers both ad-supported (AVOD) and ad-free (SVOD) subscription plans. It also features add-ons and rentals (TVOD) for premium content.
2. Peacock (NBCUniversal)
Provides a free tier with ads, a paid tier with fewer ads, and a premium ad-free tier. Occasionally, Peacock includes early access or exclusive titles for paid users.
3. Paramount+
Paramount+ has both AVOD and SVOD plans. It covers the TVOD part with in-app rentals or live PPV events. Users get to enjoy a mix of live sports, original content, and movies under one hybrid tier.
4. Amazon Prime Video
Combines a subscription model (with Prime) and TVOD for rentals or purchases. Amazon also offers free content with ads via Freevee, its AVOD service.
5. YouTube
Traditionally, YouTube was an AVOD platform, but now it includes YouTube Premium (SVOD) and movie rentals/purchases (TVOD). So, it supports all three monetization methods on a single platform.
HVOD in the VOD Ecosystem
Video on Demand (VOD) services allow viewers to watch shows and movies at their convenience, rather than following a fixed TV schedule.
There are four main monetization models for VOD platforms:
- AVOD (Ad-Supported Video on Demand): Content is free for users, but includes ads before, during, or after videos.
- SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand): Users pay a recurring fee (monthly or yearly) to access a full content library.
- TVOD (Transactional Video on Demand): Viewers pay separately to rent or buy individual videos.
- HVOD (Hybrid Video on Demand) blends these models into one platform. It gives users the freedom to choose how they want to access the content, whether with ads, through a subscription, or by paying per video. For OTT providers, it enables more ways to generate revenue.
HVOD vs TVOD vs SVOD vs AVOD
The OTT User’s Perspective
| Category | HVOD | AVOD | SVOD | TVOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access | Choose: watch free, subscribe, or pay per title | Watch for free with ads | Pay monthly/yearly for full access | Pay only for the videos you want |
| Ad Presence | Depends—ads for free content, ad-free for paid options | Ads appear before/during/after | Usually no ads, but some tiers may include | No ads at all |
| Cost to Viewer | Flexible pricing—free, subscription, or one-time payment | Free of charge | Regular recurring payment | One-time payments per video |
| Content Variety | Wide mix of free, paid, and premium content | Large selection, ad-friendly | Broad range, including original productions | Premium or exclusive titles |
| Viewer Control | High—users choose how and what to watch | Medium—ads interrupt the experience | High—watch any time, without ads | High—pay only for what you want |
The OTT Provider’s Perspective
| Category | HVOD | AVOD | SVOD | TVOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monetization | Combines revenue from ads, subscriptions, and direct purchases | Makes money from ads shown during videos | Income from subscriber payments | Earns from users buying or renting titles |
| Earning Speed | Mixed—benefits from both short-term and long-term income sources | Fast—more views mean more ad revenue | Steady and predictable with growing subscribers | Immediate income with each purchase |
| Audience Reach | Very broad—caters to free users, subscribers, and buyers | Very wide—easy entry for viewers | Limited to those willing to subscribe | Medium—appeals to those okay with one-time buys |
| Content Planning | Blend of all strategies to reach different audience types | Focus on quantity and ad-friendly content | Prioritize originals and subscriber retention | Promote premium, exclusive, or recent content |
| User Insights | Broad data across viewing habits, purchases, and ad engagement | Ad performance data, limited personalization | Detailed user behavior data from subscriptions | Minimal data—mainly purchase info |
| Churn/Drop Risk | Balanced—different options help lower cancellation risk | Very low—no ongoing commitment | Higher—users may cancel at any time | None—no subscription involved |
| Marketing Strategy | Use segmented campaigns to engage all user types effectively | Boost views for more ad income | Promote long-term benefits and exclusive content | Focus on selling specific titles |
Frequently Asked Questions
Content Writer
Anush Sargsyan is a content writer specializing in B2B content about OTT streaming technologies and digital media innovation. She creates informative, engaging content on video delivery, OTT monetization, and modern media technologies. The goal is to help readers easily understand complex ideas. Her writing is the bridge between technical detail and practical insight, making advanced concepts accessible for both industry professionals and general audiences.
Related terms
AVOD (Advertising-Based Video on Demand)
Explore how AVOD works, its monetization model, and why it's popular for free streaming platforms. Read the full definition on inorain.com glossary.
CSAI (Client-Side Ad Insertion)
Learn how CSAI delivers ads through the video player, enabling targeting, tracking, and monetization.
