VOD (Video on Demand)
What Is VOD?
VOD (Video on Demand) is a system that allows users to access video content at their convenience, using their preferred device, and without being limited by a scheduled broadcast.
With VOD, viewers can watch videos, movies, and any other content on demand, rather than being restricted to a specific time slot.
VOD Overview
1. VOD streaming allows viewers to watch pre-recorded content at any time and from anywhere. It offers convenience, a wide range of content, and accessibility across multiple devices.
2. VOD has various monetization models, including subscription-based (SVOD), transactional (TVOD), ad-supported (AVOD), and hybrid (HVOD). This means VOD can generate revenue through subscription fees, pay-per-view transactions, or advertising
3. VOD platforms utilize Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute video content globally quickly and efficiently, ensuring ease of use and device compatibility.
How VOD Works
Every VOD platform needs a well-structured tech stack that includes:
1. Content Storage: High-capacity cloud servers or on-premise systems hold video files in various resolutions.
2. Encoding/Transcoding: Videos are converted into multiple formats and bitrates to ensure compatibility across devices and bandwidths (often using H.264/H.265).
3. CDN Integration: CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) cache content closer to the user to reduce buffering and latency.
4. Video Player: HTML5, HLS/DASH support, adaptive bitrate streaming, subtitle support, DRM integration.
5. DRM and Security: Content protection via encryption and DRM (Widevine, FairPlay, PlayReady) to prevent unauthorized access.
Simply put, here is what happens:
Content gets stored on servers, and then users request to watch a video. Lastly, the system streams or downloads the content directly to their device (TV, phone, tablet, etc.).
Types of VOD
1. SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand)
In SVOD, users pay a recurring fee (monthly or annually) to gain unlimited access to a library of content.
This model is similar to a digital version of cable TV, where subscribers can watch as much content as they want during the subscription period. Netflix, Disney+, HBO Max, and Amazon Prime Video all utilize SVOD.
Monetization with SVOD:
- Recurring revenue from subscribers
- Can offer tiered pricing (e.g., HD vs. 4K plans, single vs. multiple screens)
2. TVOD (Transactional Video on Demand)
In TVOD, content is sold or rented on a per-item basis. Users pay individually for each movie, episode, or show they want to watch.
TVOD rentals typically come with time-limited access, whereas purchases offer permanent access. Apple TV, Amazon Prime Video (buy/rent), and Google Play Movies are popular platforms that offer TVOD services.
Monetization With TVOD:
- One-time transactions for rental or purchase
- Higher margins per unit but less predictable revenue
3. AVOD (Ad-Supported Video on Demand)
With AVOD, viewers can access content for free, but advertisements are inserted before, during, or after playback.
This means AVOD lowers the entry barrier for users by removing payment requirements while allowing platforms to generate income through advertising. YouTube, Tubi, Pluto TV, and Crackle are some of the platforms that offer ad-based access.
Monetization with AVOD:
- Revenue comes from advertisers
- Ads can be sold based on impressions (CPM), clicks (CPC), or actions (CPA)
- May support targeted advertising using user data
4. HVOD (Hybrid Video on Demand)
HVOD combines features of SVOD and AVOD. A platform may offer a free ad-supported tier alongside a premium, ad-free subscription. This provides flexibility for both cost-sensitive viewers and those who prefer an ad-free experience. Platforms that offer HVOD are Hulu, Peacock, Paramount+, etc..
Monetization with HVOD:
- Dual revenue streams from both ads and subscriptions
- Often used to upsell free users into becoming paying subscribers
5. PVOD (Premium Video on Demand)
PVOD delivers premium or early-access content—usually newly released films or exclusive events—at a higher-than-usual price. It’s often used as an alternative to theatrical releases or for high-profile digital debuts.
You may think it’s the same as TVOD, but it’s not entirely true
TVOD lets users rent or buy content on a pay-per-view basis, usually at standard pricing.
PVOD is a premium version of TVOD, offering early or exclusive access to new releases at a higher price.
Popular platform examples are Disney+ Premier Access, Universal Pictures' early releases, and Amazon Prime’s Premier movies that use PVOD.
Monetization with PVOD:
- High-priced one-time payments for early access
- Generates significant revenue per purchase, especially during limited-release windows
VOD Models Comparison
In general, all the platforms mentioned above are VOD platforms, each using its preferred monetization model. Let’s sum up the VOD ecosystem with a comparison table.
| Component | SVOD | TVOD | AVOD | HVOD | PVOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access Model | Subscription-based | Pay-per-view | Free with ads | Free with ads + optional subscription | One-time premium payment |
| Cost to Viewer | Monthly/annual fee | One-time fee per title | No cost | Free (with ads) or paid (ad-free) | High one-time fee |
| Ads | Usually no ads | No ads | Ads before/during/after content | Ads for free tier; none for paid tier | Usually no ads |
| Content Availability | Full catalog access | Per title | Limited selection | Mixed—some free, some paid | Exclusive or early-release titles |
| Revenue Model | Recurring subscription | Per-title purchases/rentals | Advertising revenue | Mix of ads and subscriptions | High-margin, per-title purchase |
| Examples | Netflix, Disney+, HBO Max | Apple TV, Google Play Movies | YouTube, Tubi, Pluto TV | Hulu, Peacock, Paramount+ | Disney+ Premier Access, Universal PVOD |
5 Benefits of VOD
Watch content anytime, anywhere
Stream movies, shows, podcasts, and whatever else you want on your schedule, without being tied to a broadcast time.
Control The Playback
Pause, rewind, or resume content at your convenience.
No fixed broadcast schedule
Content is available on demand, not dependent on a linear programming grid.
Device Compatibility
VOD works seamlessly on smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, laptops, and desktops. No matter what device you use, it’s compatible with VOD.
Wide content variety
Offers extensive libraries of movies, series, tutorials, and niche content catering to diverse interests.
Who Uses VOD?
Thanks to its high accessibility, VOD is widely used across different audiences and industries.
Regular consumers turn to VOD for entertainment, education, fitness, and more. They get to enjoy the flexibility of watching content on their own time.
Streaming businesses (ISPs, TV Operators, etc.) leverage VOD for internal training, marketing campaigns, and corporate communication, making it easier to deliver consistent messaging across teams.
Content creators utilize VOD platforms to monetize and distribute their videos directly to their audiences, bypassing traditional distribution channels.
Use Cases Beyond Entertainment
VOD extends far beyond movies and TV shows. For example, it’s widely used in education, powering online courses and recorded lectures on platforms like Coursera and Udemy.
Corporations use VOD for employee training, onboarding, and internal communications. The healthcare sector adopts VOD for patient education and remote consultations.
In the fitness industry, platforms like Peloton offer on-demand workout sessions. Even religious organizations use VOD to share sermons and spiritual content, making it accessible to a broader audience at any time.
VOD vs Live Streaming vs Linear TV
| Component | VOD (Video on Demand) | Live Streaming | Linear TV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viewing Flexibility | Watch anytime, on-demand | Watch in real-time only | Fixed schedule; watch at set broadcast times |
| Content Type | Pre-recorded content | Live events, shows, news, sports | Scheduled programming (TV shows, news, etc.) |
| User Control | Pause, rewind, fast-forward | Limited controls (may pause if buffered) | No playback controls |
| Device Compatibility | Available on smart TVs, phones, tablets, and web | Same as VOD (with internet access) | Primarily, TV sets via cable, satellite, or antenna |
| Internet Requirement | Yes | Yes | Not required (traditional broadcast) |
| Monetization Models | SVOD, TVOD, AVOD, PVOD | Ads, pay-per-view, subscriptions | Primarily ad-based or bundled with cable packages |
| Delivery Method | Over the internet via CDN/OTT platforms | Real-time via internet/streaming protocols | Broadcast via satellite, cable, or antenna |
| Examples | Netflix, Disney+, YouTube | Twitch, YouTube Live, Facebook Live | NBC, BBC, CNN (via cable or terrestrial signals) |
Frequently Asked Questions
Sources:
Content Writer
Anush Sargsyan is a content writer specializing in B2B content about OTT streaming technologies and digital media innovation. She creates informative, engaging content on video delivery, OTT monetization, and modern media technologies. The goal is to help readers easily understand complex ideas. Her writing is the bridge between technical detail and practical insight, making advanced concepts accessible for both industry professionals and general audiences.
Related terms
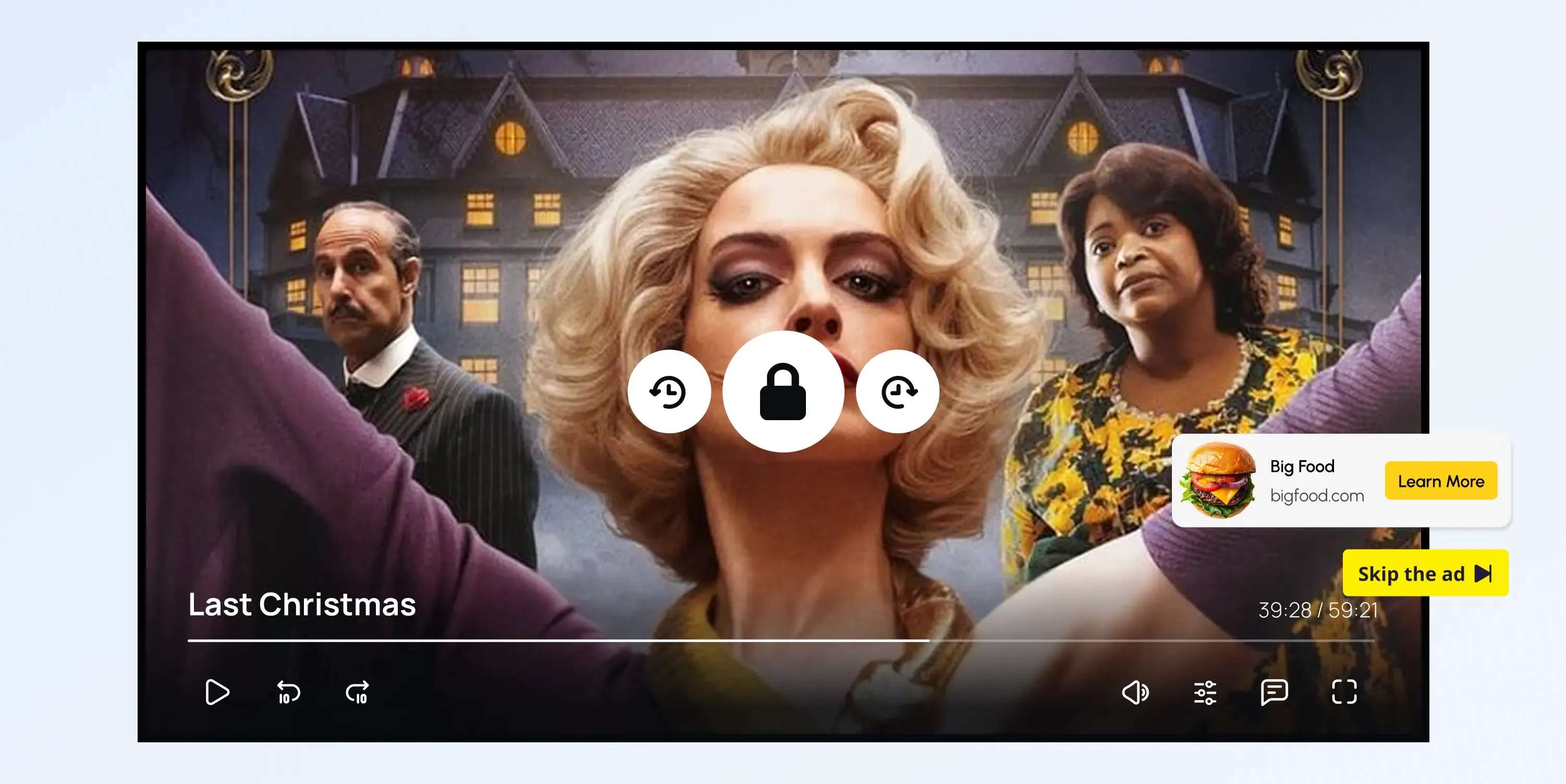
AVOD (Advertising-Based Video on Demand)
Explore how AVOD works, its monetization model, and why it's popular for free streaming platforms. Read the full definition on inorain.com glossary.
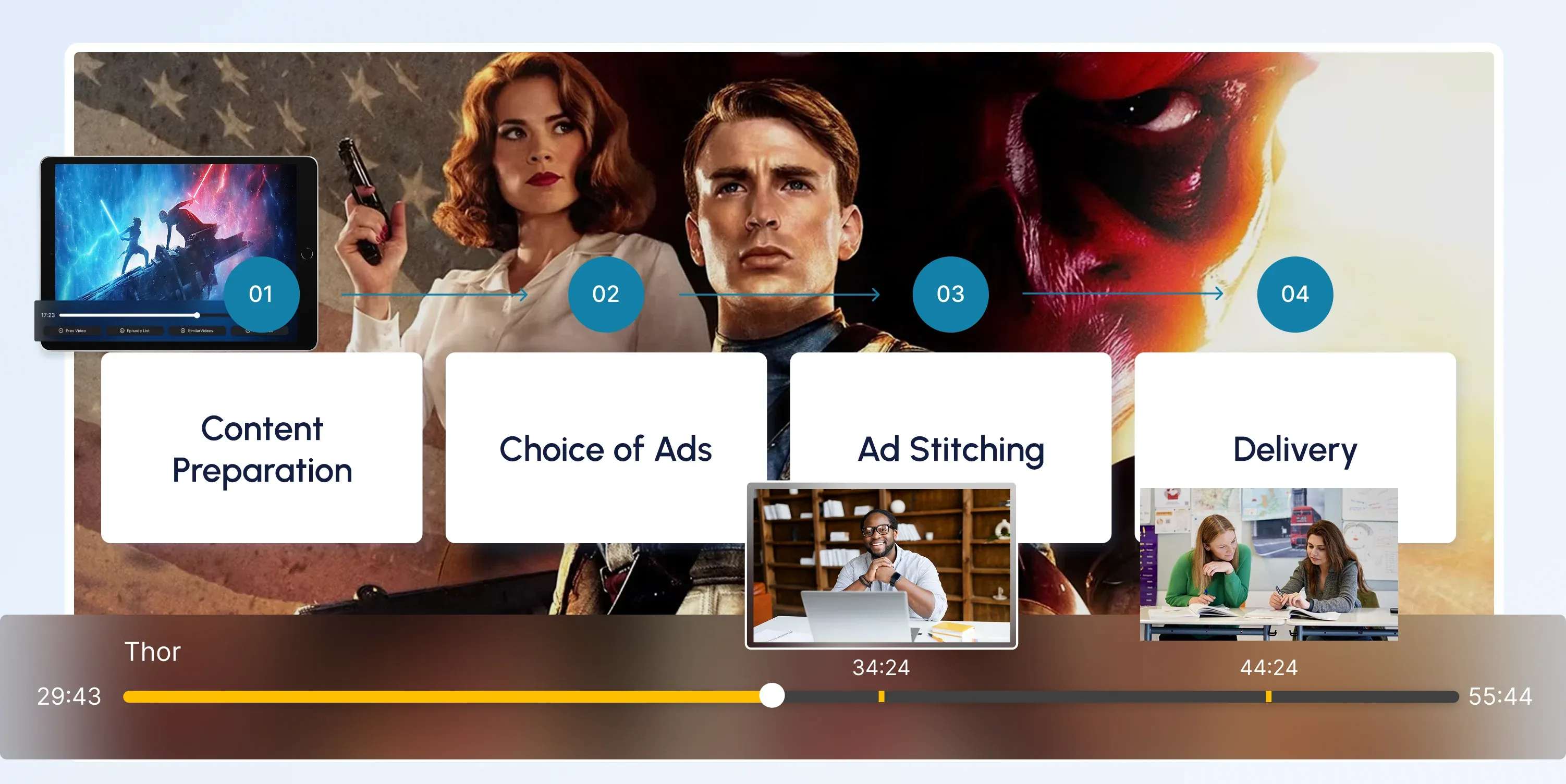
CSAI (Client-Side Ad Insertion)
Learn how CSAI delivers ads through the video player, enabling targeting, tracking, and monetization.
