
How to Develop a Video Streaming App: Best Practices
Application development can't be fully taught in a single article (especially not for a video streaming app). But we have the essential basics in one guide to help you start the right way.
So, let's learn the basics for developing a modern video streaming app.
What Is Video Streaming?
Video streaming is the process of transmitting video content over the internet in real time so viewers can watch it without downloading the entire file first.
Unlike traditional downloading, streaming allows viewers to instantly watch movies, live events, TV shows, and any other content on devices such as smartphones, computers, and smart TVs.

So, you don't have to wait for a complete download; the video is delivered in small data packets that play almost immediately while the rest of the video continues to load in the background.
And to give a complete definition of what a video streaming app is, here's what we'd say:
A video streaming app is a software application that delivers videos to viewers over the internet without requiring them to download the complete file before watching.
Now, let's get into its technical parts.
How Does it Work?
When you open a video streaming app to stream content, here is what happens behind the scenes:
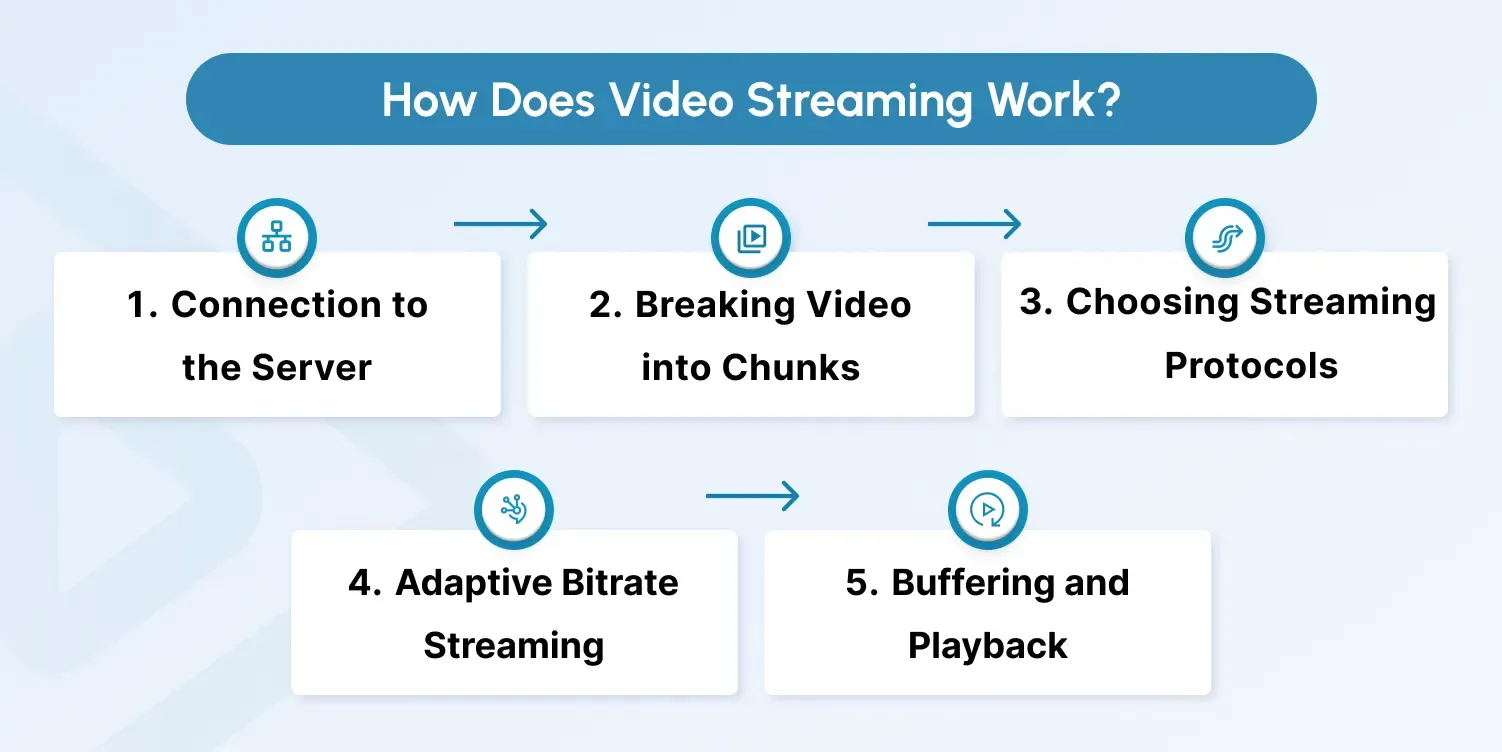
Step 1. Connection to the server
The app requests the video from a content delivery network (CDN) or streaming server. This server stores the video in a compressed digital format.
Step 2. Breaking video into chunks
After receiving the video (instead of sending a single large file), it is divided into small segments (usually 2-10 seconds each). This makes playback smoother and adaptive to changes in internet speed.
Step 3. Streaming protocols
Video streaming protocols ensure that video chunks arrive in the correct order and with the proper quality.
HLS (HTTP Live Streaming), MPEG-DASH, and RTSP are some of the popular streaming protocols.
Learn more about video streaming protocols here.
Step 4. Adaptive bitrate streaming
The app constantly checks the viewer's internet speed. If the connection slows down, it automatically switches to a lower-resolution chunk to prevent high latency. When the connection improves, it switches back to higher quality.
Step 5. Buffering and playback
The app preloads a few seconds of video into a buffer. This allows the video to start almost instantly while the rest keeps downloading in the background.
Noticed the technical coverage a single video streaming app needs? This is just the tip of the iceberg; there's a lot more to add for a smooth, enjoyable streaming experience.
Time to explore the types of video streaming apps.
Types of Video Streaming Apps
It's clear how video streaming apps generally work. Now, let's explore the different types it has.
1. On-Demand Video Streaming Apps
Video-on-Demand (VOD) platforms allow users to access pre-recorded content (stored on servers) whenever they want.
VOD apps have vast content libraries, simple navigation, and use personalized recommendations.
Examples: Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+.
2. Live Streaming Apps
Live streaming apps focus on broadcasting in real time, whether it's a concert, webinar, or gaming session. These build immediate engagement and community around live events.
The interactivity level for live streaming is the highest. It can feature real-time chat, donation, and tipping systems that engage users.
Examples: Twitch, YouTube Live, and Facebook Live.
3. OTT (Over-the-Top) Apps
OTT apps deliver video directly via the internet. These apps often combine both live and on-demand content, so you get the best of both worlds.
Examples: Netflix, Hulu, HBO Max, Apple TV+.
For anyone who wants to monetize content, OTT offers endless monetization options: SVOD (subscriptions), TVOD (transactional), AVOD (ads), hybrid (HVOD), FAST channels, and more.
OTT platforms offer flexible monetization and global reach for content owners.
If you're interested in having your own OTT app, inoRain has something for you.
4. IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) Apps
An IPTV app delivers live TV channels, video-on-demand (VOD), and time-shifted content over the internet.
Telecoms or cable operators often deploy IPTV apps to deliver digital TV over IP networks instead of traditional cable.
Types of IPTV:
- Live IPTV: Streams channels in real time.
- Time-Shifted IPTV: Lets users rewind or replay recently aired content.
- VOD IPTV: On-demand access to selected shows and movies.
10 Essential Features of a Video Streaming App
Now that you have the basics, it's perfect timing to explore the deeper, technical aspects.
Here are the core features every qualified video streaming app must have:
1. User Authentication
User authentication allows people to create secure accounts and log in safely. Encrypted passwords and extra verification steps protect personal data and prevent unauthorized access.
Example:
When you sign up, the app encrypts the password and verifies login attempts, blocking access from unknown devices.
Your encrypted password can look something like this:
$2b$12$Wm3yV7w0qY.SzRzT6mKc9O5OAgF1piZ6nA3J9c5F3i7m1FzE9e7z6
2. Content Library
A structured content library helps users browse categories, search titles, and explore new videos. A clear organization keeps navigation easy and encourages longer viewing sessions.
3. Video Player
A custom video player gives users full control over playback. They can pause, rewind, or resume a video at any time without losing their place.
Example:
The player saves the watch position so you can stop a movie halfway and continue later from the same scene.
4. Content Recommendation Engine
A recommendation engine analyzes viewing behavior to suggest relevant content. By showing you what you're likely to enjoy, the app reduces choice overload and keeps engagement high.
Example:
If you watch "Stranger Things" and "Dark", the AI engine learns you like sci-fi thrillers. It then recommends "The OA" and "Westworld" as similar titles.
5. Multiple Resolution Options
Adaptive resolution ensures smooth playback under different network conditions. The app automatically adjusts video quality to avoid buffering on slower connections.
Example: When the internet speed drops, the player switches from 1080p to 720p to keep the playback smooth.
6. Offline Viewing
Offline viewing lets users download videos and watch them without internet access. This feature is especially useful during travel or in areas with limited connectivity.
Example: You can download episodes at home and watch them later on a flight without Wi-Fi.
7. Multi-device Synchronization
Device synchronization keeps watch progress consistent across screens. You can start a video on one device and continue on another without restarting.
Example: A movie started on a Smart TV resumes on a phone at the exact same timestamp.
8. Social Integration
Social features allow you to share content, recommend shows, and interact with others. These interactions turn individual viewing into a shared and more personalized experience.
9. Payment Gateway Integration
Secure payment integration enables subscriptions and purchases through trusted methods. You can pay with multiple payment options and make encrypted transactions.
Everything is designed to be secure and convenient.
Example:
The app processes subscriptions using credit cards or digital wallets. Every transaction gets end-to-end encrypted to keep payment data private and secure.
10. Analytics Dashboard
For a minute, imagine you're a content owner who needs user insights for improvements.
An analytics dashboard provides those insights:views, engagement, audience behavior, and more.
You can use this data to improve content and grow your app.
Example:
You can check which videos get the most watch time and adjust future releases based on viewer interest.
And, if you want to do all these without going through the hustle of creating everything from scratch, we've got you. Get a white-label OTT platform ready for streaming, monetization, and growth.
Contact our experts to learn more.
Key Technologies Behind Video Streaming Apps
We covered the basics and core features; now it's time to learn about the must-have technologies for a video streaming app to come alive.
Below is a clear, practical overview with simple examples.
Streaming Protocols
Starting with the irreplaceables: video streaming protocols.
Streaming protocols define how video data travels over the internet.
When you press Play, the protocol sends the video in small chunks rather than a single large file. Your device plays the video while new pieces arrive, automatically adjusting the quality as the internet speed changes.
Video streaming protocols are similar, but each solves a specific problem and fits a different use case.
Here are the popular ones:
HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), developed by Apple, splits video into small segments and delivers them over standard HTTP. It works across most devices and adjusts smoothly to changing bandwidth.
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) is an open standard that also adapts video quality in real time. It keeps playback stable even when network conditions fluctuate.
Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP), originally created by Macromedia (later Adobe) for Flash Player, runs over TCP and focuses on low-latency streaming with minimal delay.
Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) enables peer-to-peer streaming and real-time interaction. Together, RTMP and WebRTC support low-latency delivery, making them suitable for live events and video conferencing.
Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) uses an intelligent packet retransmission method called ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request) over UDP. It protects streams from packet loss and unstable bandwidth, helping maintain high-quality live video.
Codecs
A video codec is a technology that compresses video files for delivery and then decompresses them for playback.
Without codecs, streaming high-quality video over the internet wouldn't be practical.
Codecs are a part of three main technical processes:
1. Encoding: when raw video is compressed
2. Transcoding: when multiple quality versions are created
3. Decoding: when the viewer's device plays the video
(More on these processes in the next section)
Here are the most common codecs:
H.264/AVC remains the most widely supported codec, offering reliable compression and broad device compatibility.
H.265/HEVC improves compression efficiency and can reduce bandwidth usage by up to 50% compared to H.264.
VP9, developed by Google, provides efficient compression for web streaming as an open-source option.
AV1 is a newer open-source codec that delivers even better compression, though device support is still growing.
Codec Usage Example:
A raw video is too large to stream. The codec compresses it into a smaller file so it can travel over the internet, then the viewer's device decodes it back into smooth video playback.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
First, let's understand what bitrate is.
Bitrate is the amount of data a video sends per second while it plays.
It directly affects video quality and data usage.
Higher bitrate means clearer video, but more data consumption.
Lower bitrate uses less data but reduces visual quality.
Example:
A 1080p video with a high bitrate looks sharp but uses more internet data. The same video at a lower bitrate looks softer but plays more smoothly on slower connections.
So, what does adaptive bitrate streaming mean?
Adaptive bitrate streaming adjusts video quality in real time based on network conditions.
Videos are encoded at multiple bitrates, and the player automatically switches to the best option available.
Example:
A video drops from 1080p to 720p during a slow connection, then switches back when speed improves.
Adaptive bitrate keeps playback smooth for users on both fast and unstable connections and helps prevent buffering. This is why it's a core requirement for modern streaming apps.
It's time to connect everything you learned till this point to understand encoding and transcoding.
Encoding and Transcoding
Encoding takes a raw video file and compresses it into a digital format that can be streamed over the internet.
Transcoding takes that encoded video and creates multiple versions at different qualities so the platform can adapt playback to each viewer.
These two work together to deliver the best possible playback quality during video streaming.
Now, we already know codecs are used in both encoding and transcoding. But how does everything work together?
We've made a simple breakdown for you.
Stage 1: A creator uploads a raw video. The streaming platform encodes it using H.264, turning a large file into a stream-ready format.
Stage 2: The platform then transcodes the video into multiple versions. For example, 1080p, 720p, and 480p, again using codecs like H.264, H.265, or AV1.
These versions enable adaptive bitrate streaming, allowing the player to switch quality automatically based on internet speed.
Stage 3: When a viewer presses Play, HLS or DASH delivers the video in small segments. If the connection slows down, the player switches to a lower-bitrate version to avoid buffering.
Stage 4: When the connection improves, the player switches back to a higher-quality version without interrupting playback.
Encoding prepares the video, transcoding creates flexibility, and adaptive bitrate streaming ensures smooth viewing under changing network conditions.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and P2P Streaming
A CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a network of servers placed in different locations around the world that deliver content from the nearest server to the user.
Instead of sending a video from one central server far away, a CDN serves it from a nearby location. This makes videos load faster and play more smoothly.
Example:
If a viewer in Europe watches a video, the CDN delivers it from a European server-not from a server in another continent-reducing buffering and delays.
P2P (Peer-to-Peer) is a way of delivering content where users' devices share data directly with each other instead of relying only on a central server.
In video streaming, P2P allows nearby viewers to exchange small parts of a video, reducing server load and improving delivery speed.
Example:
If several users in the same area watch the same live stream, each device shares small video segments with others. This helps the stream stay smooth even when many people watch at once.
Nowadays, CDN + P2P hybrid delivery is gaining popularity. Together, they improve playback speed, reduce buffering, and handle traffic spikes during popular events. Users get high-quality, smooth videos, and content providers reduce bandwidth costs.
Example:
During a live football match, thousands of viewers in the same city start watching at once. The CDN delivers the initial video stream, while nearby viewers share small video segments with each other in real time.
The stream stays smooth for everyone, even at peak traffic moments.
Digital Rights Management (DRM)
The final layer is security.
DRM (Digital Rights Management) is a technology that controls who can watch a video and how it can be used.
It prevents unauthorized copying, downloading, or sharing of protected content. DRM checks user permissions before playback and enforces rules like device limits, viewing time, or offline expiration.
Example:
A user can watch a rented movie inside the app, but the video stops playing if they try to copy, download, or share it outside the platform.
Step-by-Step Guide to Developing a Video Streaming App
Now you completely understand how video streaming works, what technical requirements it has, and what's irreplaceable in streaming.
Time to figure out the non-technical parts of things, connect the dots, and build the video streaming app you need.
This is where you can start:
1. Define Your Concept and Target Audience
Before you start building your app, clearly define what your streaming platform will offer and who it's for. This step sets the direction for everything that follows.
- Identify the type of content you'll provide (movies, educational videos, live events)
- Define your target audience and understand their viewing habits and preferences
- Research competitors and spot gaps in the market
- Decide whether your app will focus on live streaming, on-demand content, or both
This planning phase lays the foundation for smart development decisions and helps you build a streaming app that truly matches your audience's needs.
2. Choose the Right Technology Stack
The technologies you choose directly affect performance, scalability, and long-term maintenance. Pick tools that match your goals, budget, and growth plans.
- Frontend: React Native, Flutter, or Swift/Kotlin for mobile apps; React, Angular, or Vue.js for web apps
- Backend: Node.js, Django, Ruby on Rails, or Java Spring Boot
- Database: MongoDB, PostgreSQL, or MySQL for managing content metadata
- Cloud Services: AWS Elemental MediaLive, Google Cloud Video Intelligence, or Azure Media Services
- CDN: Cloudflare, Akamai, or Amazon CloudFront for fast content delivery
Make sure your stack supports scalability and doesn't limit you as your platform grows.
3. Design the User Interface and Experience
A clean, intuitive interface plays a huge role in keeping users engaged and coming back.
Focus on:
- A simple, easy-to-navigate layout that highlights your content
- Clear search and filtering options
- A video player that feels powerful but easy to use
- Responsive design for different screen sizes and orientations
- Accessibility features for users with disabilities
A smooth user experience makes discovering and watching content effortless-and that's what users expect.
4. Implement Core Functionality
With the basics in place, it's time to build the features that power your streaming app.
Key functionality includes:
- User authentication and profile management
- Content categorization and recommendation logic
- A reliable video player with standard controls
- Payment processing for subscriptions or purchases
- Analytics to track user behavior and content performance
This stage involves serious backend work to ensure stable streaming and secure data handling.
5. Integrate Streaming Protocols and CDN
Your delivery infrastructure directly affects video quality and playback reliability.
You'll need to:
- Implement the right streaming protocols for your content type
- Configure adaptive bitrate streaming for smooth playback
- Integrate a CDN for global content delivery
- Set up media servers for live streaming
- Use caching to reduce load times
These technical choices have a major impact on user satisfaction.
6. Implement Security Measures
Protecting your content and user data is non-negotiable. Strong security builds trust and protects your revenue.
Key measures include:
- Integrating DRM (Digital Rights Management)
- Encrypting data during transmission
- Securing authentication and authorization flows
- Applying geo-restrictions if required
- Preventing screen recording and unauthorized sharing
Solid security protects both your content and your brand reputation-without disrupting legitimate users.
7. Choose a Monetization Strategy
Decide how your app will generate revenue. Whether you use subscriptions, ads, pay-per-view, or a hybrid model, your monetization strategy should align with your content and audience expectations.
With inoRain, you get to monetize with any model you want and keep 100% of your monetization revenue. Start independent monetization with your own OTT streaming platform.
8. Test and Optimize Performance
Thorough testing ensures your app performs well in real-world conditions.
Be sure to:
- Run stress tests to evaluate performance under heavy load
- Test across devices, operating systems, and browsers
- Verify adaptive streaming under different network speeds
- Fine-tune buffering and playback behavior
- Fix performance and compatibility issues early
Remember: Careful testing prevents problems from reaching your users.
9. Launch and Gather Feedback
Once testing is complete, launch your app and let real users guide your next steps.
- Publish your app on relevant platforms and app stores
- Monitor performance metrics and user behavior
- Collect and review user feedback
- Identify improvement areas and plan updates
- Roll out regular enhancements based on real usage
Continuous improvement is essential for long-term success in a highly competitive streaming market.
Challenges in Video Streaming App Development
There are four main obstacles video streaming mostly faces, all of which involve video playback.
 Let's start with the most common one.
Let's start with the most common one.
Bandwidth Constraints
Bandwidth is how much data a network can transmit at a time.
When bandwidth is limited, videos load slowly, buffer often, or drop to low quality. High-resolution video demands more data than many networks can provide.
Here are examples of what can happen when bandwidth is limited:
- A user watches a movie on home Wi-Fi while others stream or download, and the playback keeps stopping.
- Mobile users see blurry video because their data connection cannot handle HD streaming.
- Viewers in rural areas experience long startup times before the video begins.
Latency Issues in Live Streaming
Latency is the delay between when the video is recorded and when viewers see it.
High latency makes "live" content feel late and disconnected. It breaks real-time engagement and reduces the excitement of live events.
Imagine these cases:
- A viewer hears neighbors cheering before the winning goal appears on screen.
- Live chat messages react to moments the viewer hasn't seen yet.
- Streamers and audiences struggle to interact during live Q&A sessions.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Cross-platform compatibility means the app works the same across devices, operating systems, and browsers.
Poor compatibility causes playback failures, missing features, or inconsistent controls across devices.
Here are scenarios when compatibility fails:
- A video plays on a mobile but fails to load on a Smart TV.
- Subtitles work in a browser but disappear in the mobile app.
- Older devices cannot play newer video formats at all.
Scalability Concerns
Scalability is the system's ability to handle growing numbers of users and streams.
Without it, platforms fail during peak demand. Performance drops, streams fail, and services may go offline.
Common cases:
- A live event crashes when thousands of users join at the same time.
- Video playback slows dramatically during peak hours.
- New users cannot sign up or start streams during viral traffic spikes.
Content Security
Content security protects video assets from unauthorized access, copying, and redistribution.
When content is not fully secured, premium videos leak outside the platform. Once pirated content spreads, it's nearly impossible to contain.
Here is what happens with weak security:
- A paid movie appears on free websites hours after release.
- Users share direct stream links that work without logging in.
- One subscription account gets shared across dozens of devices.
- Screen recordings of exclusive content circulate on social media.
Get Your Own Video Streaming App Without the Hustle
Yes, you can forget about all the technical issues you've just discovered with one simple move.
Partner with inoRain and let our professionals build, brand, and deliver the OTT video streaming app you need.
Your white-label OTT app will have its own CMS for centralized and fast management. You'll get features and technologies needed for secure and smooth streaming with great UI and flexible monetization.
We support both CDN and P2P streaming, optimizing bandwidth usage and keeping costs down for you.
No security issues, no wasted resources, no disappointed users. And you won't have to build everything from scratch.
Get your own streaming ecosystem, stream, monetize, and scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
Content Writer
Anush Sargsyan is a content writer specializing in B2B content about OTT streaming technologies and digital media innovation. She creates informative, engaging content on video delivery, OTT monetization, and modern media technologies. The goal is to help readers easily understand complex ideas. Her writing is the bridge between technical detail and practical insight, making advanced concepts accessible for both industry professionals and general audiences.

What is OTT? Benefits and 5 Types of OTT Services
This article has all the answers to what is an OTT platform, how OTT works and the different types of OTT services

What is OTT Analytics? Key Metrics And Tools
In this article, we uncover what OTT analytics is, the top metrics and tools required to keep your OTT platform ahead of the curve - and the competition.

What is SVOD (Subscription Video on Demand)? 2026 Guide
What is SVOD, how does it work, and why are businesses turning to SVOD platforms to create new revenue streams? This article has all the answers.
